What does a Acute Care Nurse do?
An acute care nurse plays a crucial role in healthcare settings, providing immediate and intensive care to patients with severe illnesses or injuries. This nurse works in environments like emergency rooms, intensive care units, and surgical units. They must be skilled in quick decision-making and handling life-threatening situations. The responsibilities of an acute care nurse include monitoring patient vital signs, administering medications, and coordinating care with other healthcare professionals.
Acute care nurses work closely with doctors and other medical staff to ensure patients receive the best possible care. They often work long shifts and must be prepared to handle high-pressure situations. This role requires strong communication skills to update patients and their families on their condition. Continuous education and staying updated with medical practices are also essential for an acute care nurse to provide effective care. They must be ready to act fast and use their skills to save lives and improve patient outcomes.
How to become a Acute Care Nurse?
Acute care nursing offers a dynamic and rewarding career in healthcare. To pursue this path, one must follow a clear and structured process. This journey not only requires dedication but also a commitment to continuous learning and patient care.
Below is a step-by-step guide to becoming an acute care nurse:
- Complete a nursing program. Start with an associate or bachelor's degree in nursing. Choose an accredited program to ensure quality education.
- Pass the NCLEX-RN exam. This exam is mandatory for all aspiring nurses. Prepare thoroughly to succeed and become a licensed nurse.
- Gain experience in a healthcare setting. Work in areas like emergency rooms, intensive care units, or post-operative care. This experience is essential for understanding acute care.
- Obtain acute care certification. Many acute care nurses pursue certifications through the American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN). This shows a commitment to excellence.
- Continue education and training. Stay updated with the latest in nursing practices and technologies. Attend workshops, seminars, and pursue advanced degrees if desired.
How long does it take to become a Acute Care Nurse?
Starting the journey to become an Acute Care Nurse involves several steps. First, a person needs a high school diploma or equivalent. After this, they should pursue an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) or a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN). An ADN takes about two years, while a BSN usually takes four years. Both degrees prepare students for the NCLEX-RN exam, which all nurses must pass.
Once nursing school finishes, the next step is gaining experience. Many Acute Care Nurses start in general nursing roles. Working in areas like emergency rooms or intensive care units builds the skills needed for acute care. This experience often takes one to two years. After gaining enough experience, a nurse can pursue certification in Acute Care Nursing. This step adds credibility and helps in career advancement. In total, from high school to becoming a certified Acute Care Nurse can take around five to seven years.
Acute Care Nurse Job Description Sample
An Acute Care Nurse provides specialized care to patients with acute health conditions, often in high-pressure environments such as intensive care units. This role requires advanced clinical skills, quick decision-making, and a compassionate approach to patient care.
Responsibilities:
- Assess, plan, implement, and evaluate patient care plans in collaboration with the healthcare team.
- Administer medications, treatments, and procedures as prescribed by physicians.
- Monitor and interpret patient vital signs, lab results, and diagnostic tests.
- Provide critical care to patients with life-threatening conditions, including cardiac, respiratory, and neurological emergencies.
- Collaborate with physicians, respiratory therapists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure comprehensive patient care.
Qualifications
- Registered Nurse (RN) license in the state of practice.
- Certification in Acute Care Nursing (ACNP, CCRN, or similar) preferred.
- Minimum of 2 years of experience in an acute care setting, such as ICU, ER, or critical care unit.
- Advanced knowledge of critical care nursing principles and practices.
- Strong clinical assessment, critical thinking, and decision-making skills.
Is becoming a Acute Care Nurse a good career path?
Acute Care Nurses play a crucial role in the healthcare system, specializing in the immediate and active care of patients with severe or critical health conditions. They work in fast-paced environments like emergency rooms, intensive care units, and surgical wards. Acute Care Nurses must have sharp skills in assessment, decision-making, and patient management. This role demands high levels of responsibility and quick thinking to provide the best care possible.
The career offers a variety of settings and opportunities for specialization. Nurses can work in different areas like cardiac care, trauma, and pediatric intensive care. This allows them to gain diverse experiences and skills. With experience, Acute Care Nurses can advance to leadership roles such as Nurse Manager or Clinical Nurse Specialist. The field also offers the chance to work in various locations, from urban hospitals to rural clinics.
When considering this career path, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons:
- Pros:
- High demand for qualified nurses
- Variety of work environments and specialties
- Opportunities for career advancement
- Potential for higher salaries
- Cons:
- High stress and fast-paced work
- Long and irregular hours
- Exposure to illness and emotionally challenging situations
What is the job outlook for a Acute Care Nurse?
Acute Care Nurses enjoy a promising job outlook. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports an average of 193,100 job positions available per year. This consistent demand highlights a solid career path for those entering the field. BLS data shows a 5.6% percent change in job openings from 2022 to 2032, indicating steady growth. This growth reflects the essential role of Acute Care Nurses in healthcare systems.
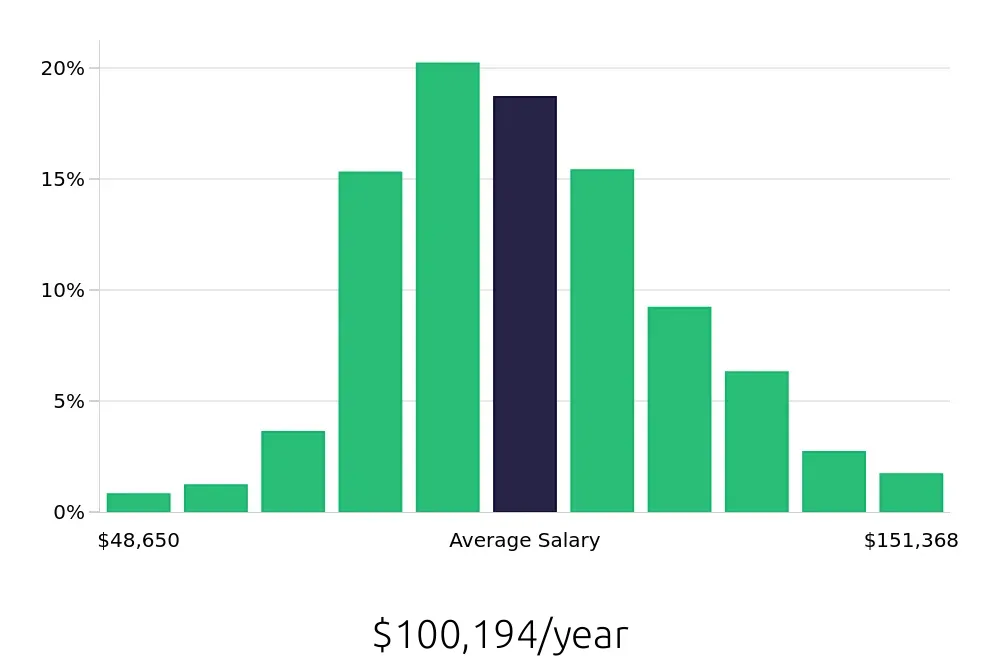
The financial benefits are attractive as well. Acute Care Nurses earn an average national annual compensation of $94,480, according to the BLS. This figure underscores the value of their expertise and dedication. Additionally, the average national hourly compensation stands at $45.42, offering competitive pay for the demanding nature of the work. These figures make Acute Care Nursing a rewarding career both professionally and financially.
Considering these statistics, job seekers can approach the Acute Care Nursing field with confidence. The combination of job stability, growth potential, and competitive compensation makes it a promising choice. Aspiring Acute Care Nurses can look forward to a fulfilling and lucrative career.
Currently 375 Acute Care Nurse job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Acute Care Nurse