What does a Audio Video Engineer do?
An Audio Video Engineer specializes in designing, installing, and maintaining audio and video systems. This professional ensures that equipment works properly and meets the needs of clients. They set up audio and video equipment for events like concerts, conferences, and weddings. They also troubleshoot and fix any issues that may arise with these systems. Attention to detail and strong problem-solving skills are essential for this role.
Responsibilities often include setting up and testing equipment before events. The engineer adjusts sound levels and video settings to achieve the best possible experience for the audience. They often work with clients to understand their needs and preferences. This role also involves working with other technicians and professionals to ensure a smooth setup. Continuous learning about new technology and equipment is important for an Audio Video Engineer to stay current in their field.
How to become a Audio Video Engineer?
Becoming an Audio Video Engineer can lead to a rewarding career in the tech world. This field combines passion for sound and vision with technical expertise. A professional in this role ensures events, concerts, and broadcasts have top-notch audio and video quality. Follow these steps to start your career in audio video engineering.
The journey to becoming an Audio Video Engineer requires dedication and the right steps. Below are essential steps to guide an aspiring professional through the process.
- Get the right education: Start with a high school diploma. Then, consider an associate or bachelor's degree in audio engineering, electronics, or a related field. These programs offer foundational knowledge and hands-on experience.
- Learn about equipment: Understand the tools and equipment used in audio video engineering. Familiarize yourself with mixing consoles, microphones, cameras, and lighting systems. Practice using these tools as much as possible.
- Gain experience: Look for internships or entry-level positions at events, studios, or production companies. This experience provides real-world knowledge and helps build a professional network.
- Certification: Consider getting certified by recognized organizations. Certifications like Certified Audio Engineer (CAE) or Professional Audio Specialist (PAS) enhance credibility and job prospects.
- Stay updated: The tech world changes fast. Keep learning about new technologies and trends. Attend workshops, webinars, and industry conferences. Continuous learning helps stay ahead in the field.
How long does it take to become a Audio Video Engineer?
Getting into audio video engineering takes time and dedication. On average, it can take two to four years to complete the necessary education and training. This includes a bachelor's degree or an associate degree in a related field. Some engineers choose to take additional courses or certifications to expand their skills.
During this time, individuals learn about sound and video systems. They study electronics, signal processing, and installation techniques. Hands-on experience is crucial. Internships or apprenticeships provide real-world practice. This helps engineers understand how to set up and troubleshoot systems in different environments. Gaining experience in various settings will improve skills and confidence.
Audio Video Engineer Job Description Sample
An Audio Video Engineer is responsible for the design, installation, and maintenance of audio-visual equipment for events, presentations, and productions. This role requires a blend of technical knowledge, problem-solving skills, and the ability to work under pressure to ensure seamless audio-visual experiences.
Responsibilities:
- Design, install, and maintain audio-visual systems for various events, including concerts, conferences, and corporate meetings.
- Set up and test audio-visual equipment, including microphones, speakers, projectors, and video displays, to ensure optimal performance.
- Troubleshoot and resolve technical issues during live events or productions, ensuring minimal disruption.
- Collaborate with clients, event coordinators, and other technical staff to understand their audio-visual needs and deliver tailored solutions.
- Stay updated with the latest audio-visual technologies and trends to recommend and implement improvements to existing systems.
Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in Audio Engineering, Electronics, or a related field.
- Proven experience as an Audio Video Engineer or similar role, with a strong portfolio of completed projects.
- Proficiency in operating and maintaining a wide range of audio-visual equipment, including microphones, speakers, projectors, and video conferencing systems.
- Strong problem-solving skills and the ability to think quickly under pressure.
- Excellent communication skills, with the ability to explain technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
Is becoming a Audio Video Engineer a good career path?
An Audio Video Engineer works with the technology behind sound and video systems. This role involves designing, installing, and maintaining these systems. The job suits someone who enjoys working with technology and solving problems. These engineers find work in many places, including theaters, concert venues, and corporate offices.
Being an Audio Video Engineer offers many benefits. The job often provides a steady income. Many companies and organizations need these systems. This can lead to job security. The work also allows for creativity. Each project has unique challenges that require new solutions. Travel is another perk. Engineers often visit different sites to set up or fix systems.
However, there are some drawbacks to consider.
- Long Hours: Projects often take more time than expected. This can lead to long hours.
- Travel: While travel can be exciting, it can also mean being away from home for long periods.
- Physical Demands: The job can be physically demanding. Engineers may need to lift heavy equipment or work in cramped spaces.
- Technical Skills: The field is always changing. Engineers must keep up with new technology.
What is the job outlook for a Audio Video Engineer?
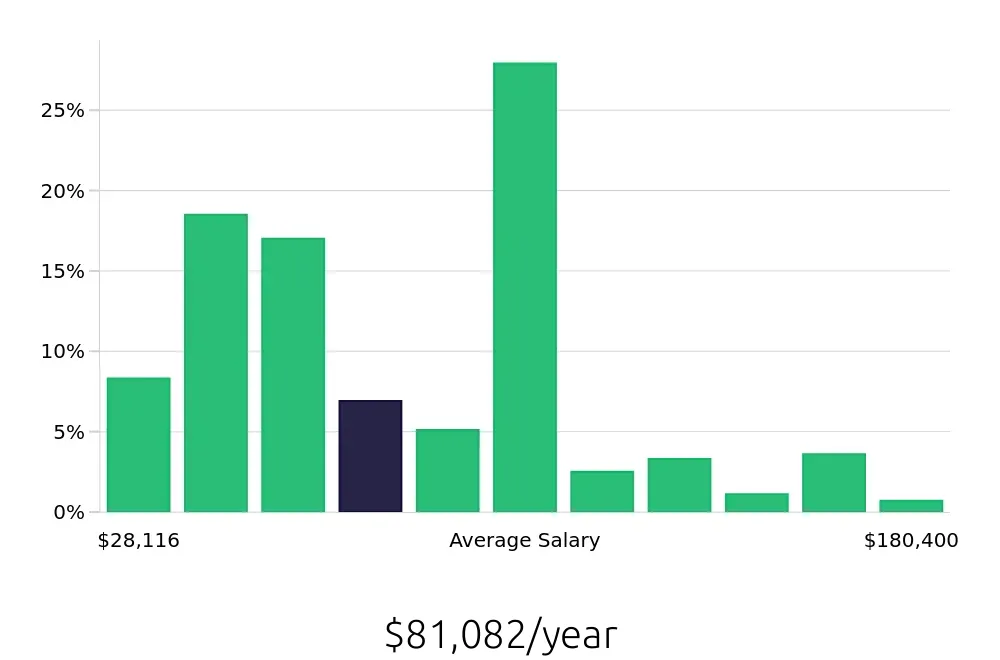
The job market for Audio Video Engineers is showing promising trends, with an average of 12,900 positions opening each year, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). This consistent demand highlights the growing need for skilled professionals in this field. The BLS also reports a projected growth rate of 1.7% from 2022 to 2032, indicating a stable job outlook for those entering the industry.
For job seekers, the financial outlook in this field is encouraging as well. The BLS states that the average national annual compensation for Audio Video Engineers is $65,010, with an hourly rate of $31.26. These figures suggest a rewarding career both in terms of job stability and compensation. With the right skills and experience, professionals in this role can expect to earn a competitive salary.
Considering the steady demand and favorable compensation, pursuing a career as an Audio Video Engineer is a smart choice. The industry’s growth, coupled with attractive salary packages, makes this field a valuable option for those seeking long-term employment and professional growth.
Currently 26 Audio Video Engineer job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Audio Video Engineer