What does a Biomedical Engineer do?
A Biomedical Engineer blends the principles of engineering with the sciences to improve health care. This professional works on designing and creating medical equipment, software, and devices. They strive to improve existing products and develop new ones. Their work helps in diagnosing, monitoring, and treating medical conditions. Biomedical Engineers collaborate with doctors and other health professionals to understand medical needs and translate them into engineering solutions.
Daily tasks of a Biomedical Engineer may include analyzing data, conducting research, and testing prototypes. They might also work on improving existing devices to make them more efficient and user-friendly. In addition, they often need to prepare detailed reports and documentation of their findings and designs. The role demands strong problem-solving skills, attention to detail, and the ability to work in teams. It is a dynamic field with opportunities to make a real difference in people's lives through innovative solutions.
How to become a Biomedical Engineer?
Becoming a biomedical engineer involves several key steps. It's a rewarding career that combines knowledge of biology, medicine, and engineering. This guide covers the essential steps to start a career in this field.
Below are the steps to become a biomedical engineer:
- Earn a bachelor’s degree in biomedical engineering or a related field, such as mechanical or electrical engineering. This will give the necessary knowledge in both biology and engineering.
- Gain practical experience through internships or part-time jobs in healthcare or engineering. This helps to understand the real-world applications of biomedical engineering.
- Pursue a master’s degree in biomedical engineering for advanced knowledge and better job opportunities. Many employers prefer candidates with a master’s degree.
- Consider getting a Ph.D. if planning to work in research or academia. A Ph.D. can open more advanced career paths and opportunities for leadership roles.
- Obtain the necessary certifications and licenses. Some states require biomedical engineers to be licensed. Certifications can also enhance professional credentials.
How long does it take to become a Biomedical Engineer?
Interested in a career as a Biomedical Engineer? This path leads to a rewarding job, combining biology, engineering, and technology. It takes dedication, but the time spent is worth it. Most people need a bachelor's degree, which takes four years. Some positions may ask for a master's degree, adding two more years.
Getting the right education is key. Start with a strong high school background in math, science, and technology. Attend a college or university that offers biomedical engineering programs. These programs mix classes in biology, engineering, and chemistry. Some schools offer co-op programs, letting students work with companies during their studies. This hands-on experience can be very helpful.
Biomedical Engineer Job Description Sample
We are seeking a highly skilled and innovative Biomedical Engineer to join our dynamic team. The ideal candidate will have a strong background in bioengineering and a passion for developing advanced medical technologies. This role will involve designing, developing, and testing medical equipment and devices to improve patient care and outcomes.
Responsibilities:
- Design, develop, and test medical devices and equipment.
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams to ensure product design meets regulatory standards and customer needs.
- Conduct research and analysis to identify new opportunities for product improvement and innovation.
- Prepare technical documentation and reports on project progress and outcomes.
- Assist in the development and implementation of quality control procedures.
Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in Biomedical Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, or a related field.
- Proven experience in biomedical engineering, preferably in a manufacturing or product development setting.
- Strong understanding of medical device design principles and regulatory requirements.
- Proficiency in CAD software and other engineering tools.
- Excellent problem-solving skills and attention to detail.
Is becoming a Biomedical Engineer a good career path?
Biomedical Engineers combine their skills in biology, medicine, and engineering. They design equipment and software used in health care. This work includes medical devices, prosthetics, and systems to monitor health. They make tools to help doctors and patients. This field offers many exciting job opportunities and the chance to improve health care.
Interested in becoming a Biomedical Engineer? Consider these pros and cons. On the plus side, the job offers good pay. Many opportunities exist in hospitals, research labs, and medical device companies. Biomedical Engineers often enjoy a flexible schedule and the chance to make a real difference in people's lives. However, this career also has challenges. Long hours and high stress can be part of the job. Working with complex equipment also requires constant learning. Despite these challenges, the rewards can be very fulfilling.
Think about your interests and skills. If you enjoy solving problems and working with medical equipment, this could be a great career. Biomedical Engineers play a key role in health care, helping to develop new technologies and improve patient care.
Here are some more details about what to expect:
- Pros:
- High salary potential
- Many job opportunities
- Chance to make a difference in health care
- Opportunities for continuous learning and development
- Cons:
- Long and stressful work hours
- High level of responsibility
- Constant need to update skills and knowledge
- Exposure to complex and sometimes risky equipment
What is the job outlook for a Biomedical Engineer?
The job outlook for Biomedical Engineers remains strong, with an average of 1,200 job positions available each year, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). This steady demand offers promising career prospects for those entering the field. The industry expects a 5.1% increase in job openings from 2022 to 2032, highlighting continued growth and stability. Aspiring Biomedical Engineers can look forward to a rewarding career with ample opportunities.
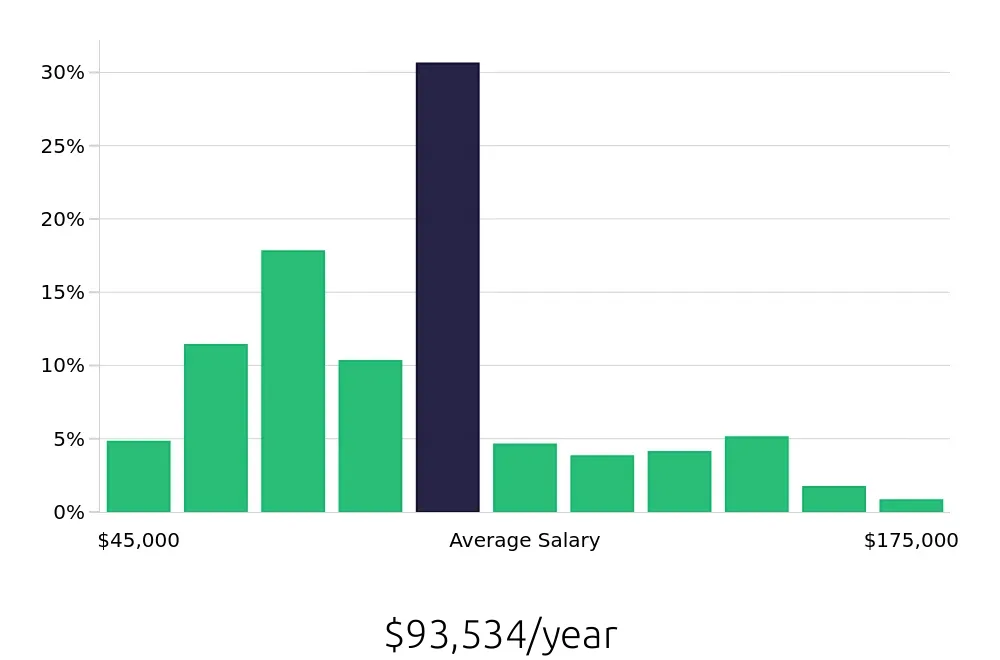
Biomedical Engineers enjoy a competitive salary, with an average national annual compensation of $106,700, as reported by the BLS. This attractive pay reflects the high level of skill and expertise required in the field. The average hourly compensation stands at $51.30, further emphasizing the financial benefits of a career in biomedical engineering. Job seekers will find this profession both lucrative and fulfilling.
To thrive in this career, individuals should focus on gaining relevant education and skills. This includes pursuing degrees in biomedical engineering or related fields, along with hands-on experience in labs and medical settings. Continuous learning and staying updated with the latest technological advancements will also help in securing and advancing within these promising job positions. With the right preparation, job seekers can successfully navigate the competitive landscape and build a successful career in biomedical engineering.
Currently 44 Biomedical Engineer job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Biomedical Engineer