What does a Editor do?
An editor reviews and improves written content. They ensure the text is clear and free of errors. An editor checks grammar, spelling, and punctuation. They also make sure the content follows a consistent style and tone. Editors often suggest changes to improve the flow and readability of the text. They may also suggest changes to the structure or content to enhance its impact.
Editors work with a variety of materials. They may edit articles, books, blogs, or marketing materials. Editors often collaborate with writers to refine their work. They provide feedback and make necessary changes. This role requires attention to detail and a strong understanding of language. Editors must also have good communication skills to effectively work with writers. This position is ideal for those who enjoy working with words and helping others communicate effectively.
How to become a Editor?
Becoming an editor involves several key steps that build a strong foundation in language arts and editing skills. This profession requires attention to detail and a passion for refining content. Follow these steps to embark on a successful career as an editor.
First, obtain a relevant degree. Many editors hold a degree in English, journalism, or communications. This education provides essential knowledge of grammar, style, and storytelling. Completing a degree program enhances job prospects and demonstrates a commitment to the field.
- Gain experience through internships or entry-level positions. Practical experience is crucial. Look for internships or part-time jobs at publishing houses, magazines, or online media companies. This hands-on experience teaches real-world editing skills and helps build a professional network.
- Develop a portfolio. Showcase your skills by creating a portfolio of edited work. Include articles, blog posts, or other writing samples. Highlight your ability to correct errors, improve clarity, and enhance overall quality. A strong portfolio can set you apart from other candidates.
- Improve technical skills. Familiarize yourself with editing software and tools. Programs like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, and specialized editing software are common in the industry. Proficiency in these tools can make you more efficient and effective in your work.
- Network with professionals. Attend industry events, join professional organizations, and connect with other editors online. Building relationships can lead to job opportunities and valuable advice. Networking is a key part of career growth in any field.
- Continue learning and adapting. The field of editing is always evolving. Stay updated with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices. Consider taking courses or attending workshops to keep your skills sharp. Adaptability is essential for long-term success as an editor.
How long does it take to become a Editor?
Becoming an editor takes time and dedication. Most editors start with a bachelor’s degree in English, journalism, or a related field. This degree usually takes about four years. A degree provides the basics of writing, grammar, and editing. After graduation, some editors gain experience by working as writers or assistants. This hands-on work helps them learn more about the industry.
Experience plays a big role in becoming an editor. Some editors need a few years of experience. Others may need more, especially if they want to work in a specific area, like publishing or marketing. Many editors start as freelance editors. This allows them to build a portfolio. A strong portfolio can help editors get better jobs. Editors who want to move up often take extra courses. These courses cover specialized editing skills or new technologies. Continuing education can make an editor more valuable to employers.
Editor Job Description Sample
We are seeking a detail-oriented and creative Editor to join our team. The ideal candidate will be responsible for ensuring the quality, accuracy, and coherence of written content across various platforms. This role requires a keen eye for detail, strong communication skills, and the ability to manage multiple projects simultaneously.
Responsibilities:
- Review and edit written content for clarity, grammar, punctuation, spelling, and consistency.
- Collaborate with writers, content creators, and other team members to ensure content aligns with the brand's voice and guidelines.
- Identify and correct inconsistencies in tone, style, and format.
- Develop and maintain style guides to ensure uniformity across all content.
- Ensure all content adheres to editorial standards and guidelines.
Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in English, Journalism, Communications, or a related field.
- Proven experience as an Editor or similar role.
- Exceptional grammar, punctuation, and spelling skills.
- Strong understanding of editorial processes and publishing standards.
- Ability to handle multiple projects and meet deadlines.
Is becoming a Editor a good career path?
Being an editor means crafting stories, articles, and books to make them clear and engaging. Editors read and revise content, check facts, and ensure the work follows style guides. They work in many areas like publishing, journalism, and marketing. Editors help writers share their ideas effectively.
Choosing this career has its ups and downs. Here are some points to consider:
- Pros:
- Helps shape important stories and information.
- Gives a chance to work with many talented writers.
- Offers a chance to focus on details and improve texts.
- Cons:
- Can be a demanding job with tight deadlines.
- May require long hours, especially during big projects.
- Income can vary widely based on experience and industry.
What is the job outlook for a Editor?
The job outlook for Editors is steady, with an average of 31,800 job positions expected each year. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the job openings for Editors are projected to increase by 1.3% from 2022 to 2032. This indicates a stable and growing demand for skilled Editors in the industry. Job seekers can look forward to opportunities in various sectors, including publishing, media, and digital content creation.
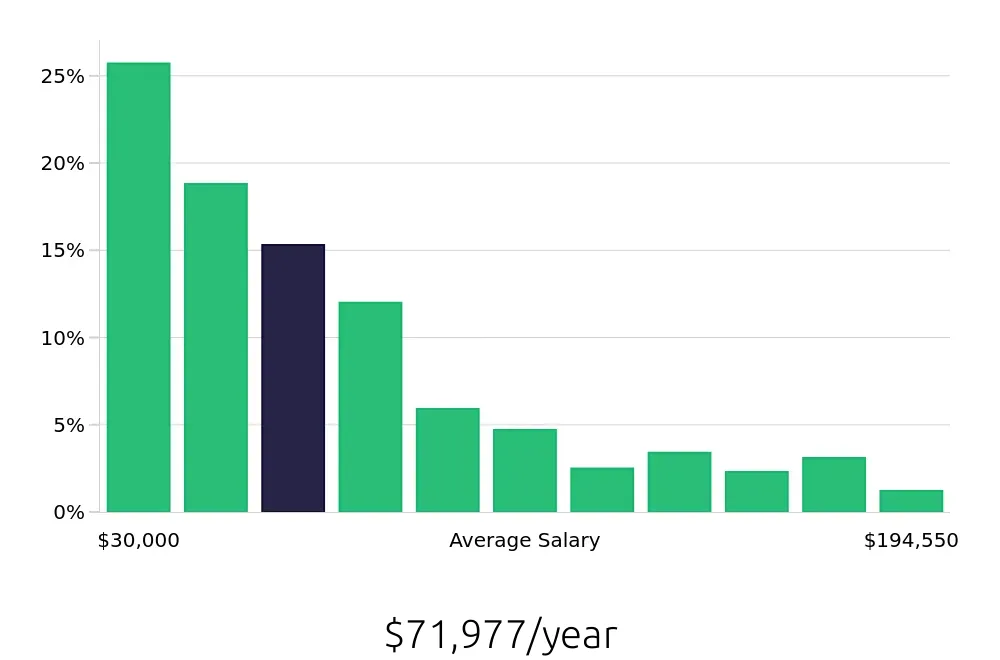
Editors play a crucial role in shaping the content that reaches the public. They ensure that articles, books, and other forms of media are well-written, accurate, and engaging. With the rise of digital media, the demand for Editors who can manage online content is particularly strong. This trend suggests a positive job market for those with strong writing, editing, and communication skills. The average national annual compensation for Editors is $86,120, and the hourly rate is $41.4, according to the BLS.
The growing need for quality content across different platforms presents a great opportunity for job seekers. Editors who can adapt to new technologies and content management systems will find themselves in high demand. With the increasing importance of digital media, Editors who can work with both traditional and online content will have a competitive edge. The combination of a steady job outlook and competitive compensation makes this a promising career path for aspiring Editors.
Currently 390 Editor job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Editor