What does a Epidemiologist do?
An epidemiologist studies how diseases spread. This professional collects data and conducts research to understand why some people get sick while others do not. They look at patterns and use this information to develop ways to stop diseases from spreading. This work helps protect communities and save lives.
Epidemiologists work in many different places. They can be found in hospitals, research labs, and government agencies. These professionals gather information from doctors, patients, and other sources. They analyze this data to find trends and causes of diseases. Epidemiologists create reports and recommendations based on their findings. They share this information with public health officials and the medical community. This helps guide efforts to prevent and control diseases.
How to become a Epidemiologist?
Becoming an epidemiologist involves a structured path that starts with foundational education and moves toward specialized training and experience. This journey allows individuals to study disease patterns and contribute to public health. Here is a step-by-step guide to starting a career in epidemiology.
First, obtain a bachelor's degree in a science-related field, such as biology or chemistry. This provides essential knowledge of the sciences needed in epidemiology. Next, pursue a master's degree in public health (MPH) with a concentration in epidemiology. This degree teaches important skills in disease research and analysis. Then, gain practical experience through internships or entry-level positions in public health. Working under experienced professionals helps to build skills and understand real-world applications.
After accumulating experience, epidemiologists often take on more responsibility, such as leading research projects or public health initiatives. Finally, consider obtaining a Doctor of Public Health (DrPH) or a PhD in epidemiology for advanced positions. These degrees offer deeper insights and can lead to roles in teaching or high-level research.
- Earn a bachelor's degree in science.
- Complete a master's degree in public health.
- Gain experience through internships or jobs.
- Advance in responsibilities and roles.
- Pursue advanced degrees for higher positions.
How long does it take to become a Epidemiologist?
Interested in public health and disease control? Consider a career as an epidemiologist. This path involves studying disease patterns to find ways to prevent them. To start, a bachelor's degree in a science field is the first step. This usually takes four years.
After earning a bachelor's degree, the next step is a master's degree in public health (MPH) or a related field. This advanced degree takes about two years to complete. During this time, students focus on courses related to epidemiology. They learn about statistics, research methods, and disease control. Some epidemiologists choose to go further with a Ph.D. or a Doctor of Public Health (DrPH). These advanced degrees can take an additional three to five years. Completing these steps leads to a rewarding career in protecting public health.
Epidemiologist Job Description Sample
As an Epidemiologist, you will be responsible for analyzing data and conducting research to understand the patterns, causes, and effects of disease and injury in specific populations. This role involves collaborating with healthcare professionals, government agencies, and community organizations to develop strategies for disease prevention and control.
Responsibilities:
- Conduct research to identify the causes, distribution, and control of disease within populations.
- Analyze data from various sources, including medical records, laboratory reports, and public health surveys.
- Design and implement epidemiological studies to investigate health-related issues.
- Develop and recommend public health policies based on research findings.
- Collaborate with healthcare professionals, government agencies, and community organizations to address public health issues.
Qualifications
- A minimum of a Master's degree in Epidemiology, Public Health, or a related field.
- Strong analytical skills with the ability to interpret complex data.
- Excellent research and problem-solving skills.
- Proficiency in statistical software and data analysis tools.
- Strong written and verbal communication skills.
Is becoming a Epidemiologist a good career path?
Epidemiologists study the patterns, causes, and effects of disease conditions identified as health events in defined populations. This career combines health science, statistics, and biology. Working in public health, epidemiologists seek to understand how diseases spread and how to prevent them. They use data to predict outbreaks and inform health policies.
The path to becoming an epidemiologist typically involves a college degree in a health-related field, such as biology, medicine, or public health. Many epidemiologists then pursue a master’s degree in public health (MPH). Some positions may require a Ph.D. or a Doctor of Public Health (DrPH). Real-world experience through internships or research projects is valuable. Epidemiologists often work for government agencies, universities, or healthcare organizations.
Working as an epidemiologist offers several benefits. Epidemiologists make a good salary. They play a crucial role in protecting public health. They get to use data to solve health mysteries. They can travel for fieldwork. However, there are challenges. The work can be stressful, especially during outbreaks. It requires a lot of education and training. Job opportunities may vary by region. The field can be competitive.
Consider these pros and cons before pursuing this career:
- Pros:
- Good salary
- Protect public health
- Use data to solve health issues
- Opportunities to travel
- Cons:
- Stressful during outbreaks
- Requires extensive education
- Variable job opportunities
- Competitive field
What is the job outlook for a Epidemiologist?
Job seekers interested in becoming an epidemiologist have reason to be optimistic. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports around 8,300 positions available each year. This steady number provides consistent opportunities for those entering the field. With an average of 11% growth projected from 2022 to 2032, the field is expected to expand. This growth highlights the increasing need for professionals who can study and prevent disease outbreaks.
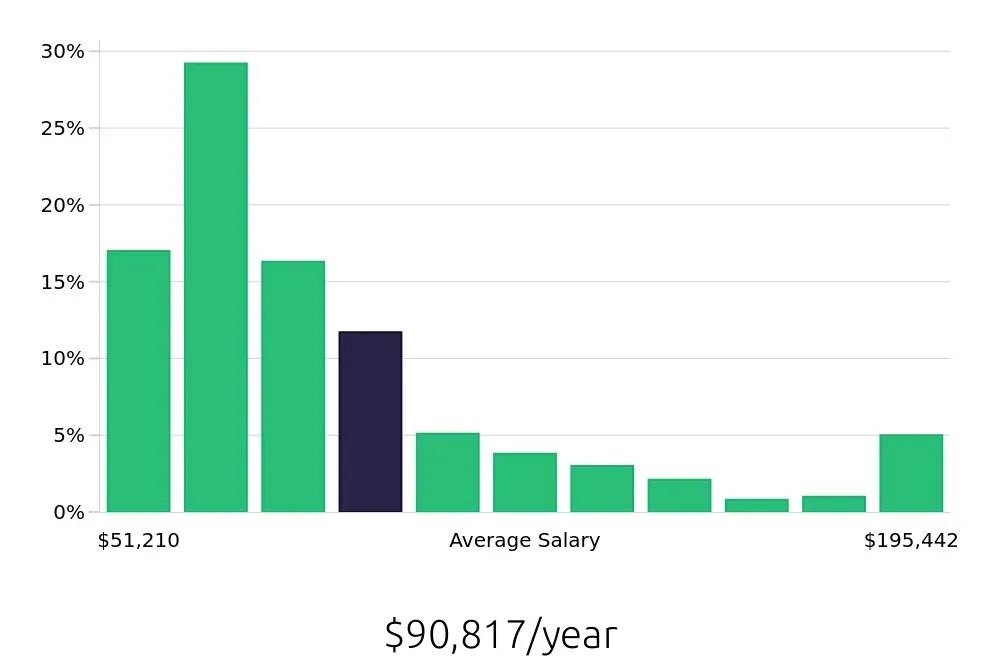
Epidemiologists enjoy a competitive average annual salary of $110,850, according to BLS data. This pay reflects the specialized knowledge and skills required for the job. With an average hourly wage of $53.29, this field offers a lucrative career. High demand and rewarding pay make epidemiology an attractive choice for job seekers.
The demand for skilled epidemiologists continues to rise. Public health concerns and the need for disease prevention drive this demand. Job seekers in this field can expect a stable job market with growth potential. The combination of a growing job market and attractive compensation makes epidemiology a promising career choice.
Currently 50 Epidemiologist job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Epidemiologist