What does a Licensed Practical Nurse do?
A Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) plays a vital role in patient care. They work under the supervision of doctors and registered nurses. LPNs provide basic medical care to patients. They check vital signs, administer medications, and assist with daily activities. LPNs also help in dressing wounds and monitoring patients' conditions. They often work in hospitals, nursing homes, and clinics.
LPNs must have strong communication skills. They interact with patients, families, and healthcare teams. LPNs need to be detail-oriented and compassionate. They ensure patients receive the care they need. LPNs also keep records of patient health information. They work in shifts, which may include nights, weekends, and holidays. This role is essential for the smooth operation of healthcare facilities.
How to become a Licensed Practical Nurse?
Becoming a Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) offers a rewarding career path in healthcare. LPNs play a crucial role in patient care, working under the supervision of doctors and registered nurses. This profession requires dedication, compassion, and a commitment to healthcare. Follow these steps to embark on a successful journey to becoming an LPN.
The journey to becoming an LPN involves several key steps. Each step is designed to ensure you gain the necessary skills and knowledge to excel in this vital role. Below is an outline of the process:
- Complete a State-Approved LPN Program: Enroll in a practical nursing program accredited by your state's nursing board. These programs typically last one year and include both classroom instruction and clinical training.
- Pass the NCLEX-PN Exam: After completing the LPN program, take and pass the National Council Licensure Examination for Practical Nurses (NCLEX-PN). This exam tests your knowledge and skills in nursing care.
- Apply for State Licensure: Submit an application for licensure to your state's nursing board. This process includes providing proof of your education and exam results. Once approved, you will receive your LPN license.
- Gain Clinical Experience: Seek employment in healthcare settings such as hospitals, nursing homes, or clinics. Practical experience is essential for developing your skills and building your professional network.
- Consider Continuing Education: Stay updated with the latest nursing practices and technologies. Many LPNs pursue additional certifications or advanced degrees to enhance their career opportunities.
How long does it take to become a Licensed Practical Nurse?
The journey to becoming a Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) involves a mix of education and training. Most programs take about one to two years to complete. These programs combine classroom instruction with hands-on clinical experience. The curriculum covers essential nursing skills and medical knowledge. Graduates must then pass the NCLEX-PN exam to earn their license.
LPNs can start their careers faster than many other healthcare professionals. This makes it an attractive option for those eager to enter the field. The time commitment is shorter than that of a Registered Nurse (RN). However, the quality of training remains strong. LPNs play a vital role in patient care. They work under the supervision of doctors and RNs. Their responsibilities include taking vital signs, administering medications, and providing basic patient care. This career path offers a rewarding way to help others while entering the workforce sooner.
Licensed Practical Nurse Job Description Sample
We are seeking a compassionate and skilled Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) to join our healthcare team. The LPN will provide essential nursing care to patients, working under the supervision of registered nurses and physicians. This role requires a commitment to patient care and the ability to work in a fast-paced environment.
Responsibilities:
- Provide basic nursing care to patients, including taking vital signs, administering medications, and dressing wounds.
- Assist in the development and implementation of patient care plans.
- Monitor and document patient conditions and report any changes to the supervising nurse or physician.
- Collaborate with healthcare team members to ensure comprehensive patient care.
- Educate patients and their families on health conditions and care plans.
Qualifications
- Current and valid LPN license in the state of [State].
- Graduate of an accredited practical nursing program.
- Minimum of [X] years of experience in a clinical setting preferred.
- Strong clinical skills and attention to detail.
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills.
Is becoming a Licensed Practical Nurse a good career path?
A career as a Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) offers a rewarding path in healthcare. LPNs work closely with patients, providing essential care and support. They often find jobs in hospitals, nursing homes, and clinics. This role allows LPNs to make a direct impact on people's lives every day.
LPNs enjoy several benefits. They can enter the workforce quickly, often with just a one-year program. The demand for LPNs remains high, ensuring job stability. LPNs also have the opportunity to advance their careers with further education. However, they should be aware of some challenges. LPNs may work long hours, including nights and weekends. The job can be physically demanding and emotionally taxing. Despite these challenges, many find the work deeply fulfilling.
Consider these pros and cons before pursuing a career as an LPN:
- Pros:
- Short training period
- High job demand
- Opportunities for career advancement
- Cons:
- Long and irregular hours
- Physical and emotional demands
What is the job outlook for a Licensed Practical Nurse?
The job outlook for Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs) is promising, with an average of 54,400 job positions available each year. This steady demand reflects a growing need for healthcare professionals. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) predicts a 5.3% increase in job openings from 2022 to 2032. This growth rate indicates a stable and expanding career path for LPNs.
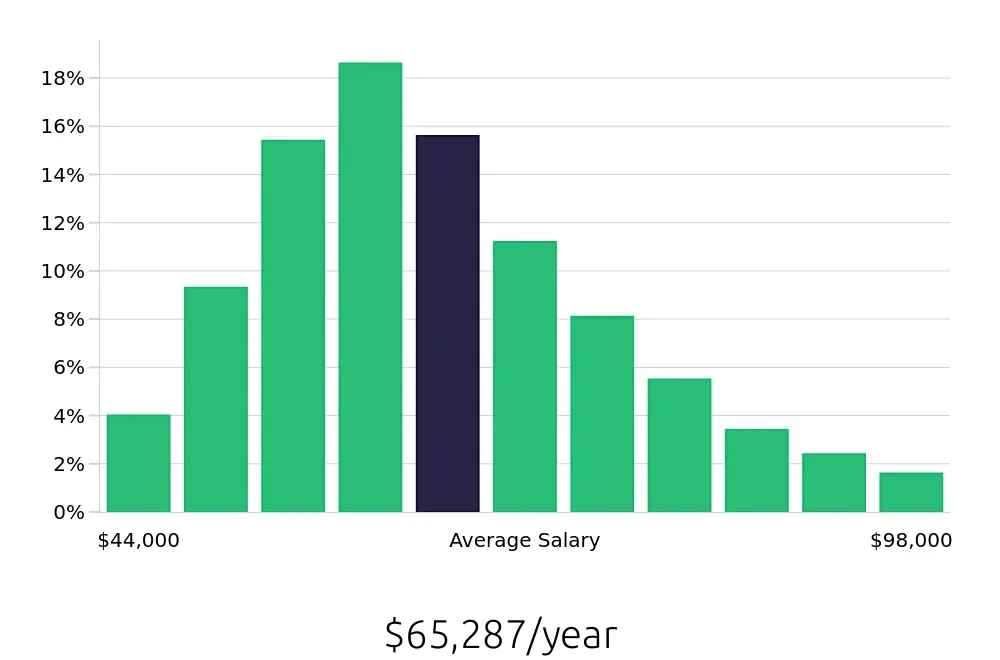
LPNs enjoy a competitive average annual salary of $60,790. This compensation reflects the essential role LPNs play in patient care. Hourly, LPNs earn an average of $29.23, providing a reliable income. The BLS data highlights the financial stability and growth potential in this field. LPNs can expect both job security and the opportunity to advance their careers.
For job seekers, the LPN field offers a blend of job security, competitive pay, and growth opportunities. With an average of 54,400 job positions per year and a projected 5.3% increase in openings, LPNs can look forward to a stable career. The average annual salary of $60,790 and hourly wage of $29.23 provide financial stability and room for advancement. This makes LPN a rewarding career choice for those entering the healthcare industry.
Currently 23,753 Licensed Practical Nurse job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Licensed Practical Nurse