What does a Microbiologist do?
A Microbiologist studies microorganisms, which include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. They aim to understand how these tiny life forms interact with each other and their environment. Microbiologists work in various fields, such as healthcare, food safety, and environmental science. They often conduct experiments in labs, analyze samples, and develop methods to control or prevent infections.
The role of a Microbiologist involves several key responsibilities. They identify and classify different microorganisms. This can help in diagnosing diseases and understanding how they spread. They also develop new treatments and vaccines by studying how microorganisms cause illnesses. Microbiologists often work with other scientists to discover new ways to use microorganisms for beneficial purposes, such as in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals. Their work helps improve public health and safety by preventing and controlling infectious diseases.
Key tasks of a Microbiologist include:
- Conducting laboratory tests
- Analyzing data and results
- Writing reports and research papers
- Collaborating with other scientists
- Maintaining laboratory equipment
How to become a Microbiologist?
Becoming a microbiologist involves a series of steps that combine education, practical experience, and specialized knowledge. This career offers opportunities to explore the microscopic world and its impacts on health, the environment, and industry. Below are the essential steps to embark on this career path.
Starting with the right educational foundation is crucial. A bachelor’s degree in microbiology, biology, or a related field is a must. This degree provides the fundamental knowledge needed to understand microorganisms and their interactions. During the undergraduate studies, students should focus on courses that cover cellular biology, genetics, and chemistry. Gaining experience through internships or research projects is also important. It helps to apply classroom knowledge in real-world settings.
- Obtain a bachelor’s degree in microbiology or a related field.
- Gain practical experience through internships or research projects.
- Consider pursuing a master’s or doctoral degree for specialized knowledge.
- Obtain certifications that may be required or beneficial in the field.
- Seek employment opportunities in laboratories, research institutions, or industry.
Pursuing advanced degrees can enhance career prospects. A master’s or doctoral degree in microbiology allows for deeper research and specialization. These advanced degrees often include opportunities to work on research projects and publish findings. Certifications in areas such as laboratory safety or specific techniques can also be valuable. They show commitment to the profession and can open up more job opportunities.
How long does it take to become a Microbiologist?
The journey to becoming a microbiologist involves several steps. First, one needs a bachelor's degree in microbiology or a related field. This typically takes four years. During this time, students learn about bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. They also take courses in chemistry, physics, and biology.
After earning a bachelor's degree, most microbiologists pursue a master's degree. This adds another two to three years. A master's degree allows for more specialized study. It includes advanced research and lab work. Some microbiologists also choose to get a Ph.D. This adds another three to five years. A Ph.D. prepares them for careers in research or higher education.
Microbiologist Job Description Sample
We are seeking a highly skilled Microbiologist to join our research team. The ideal candidate will have a strong background in microbiology, with a focus on laboratory research and data analysis. This role involves conducting experiments, analyzing microbial samples, and contributing to scientific publications.
Responsibilities:
- Conduct laboratory experiments to study microbial organisms.
- Analyze and interpret data from microbiological tests and experiments.
- Maintain detailed records of experiments and findings.
- Collaborate with other scientists and researchers to develop new hypotheses and research directions.
- Ensure compliance with safety protocols and laboratory standards.
Qualifications
- A Ph.D. in Microbiology, Biology, or a related field.
- Proven experience in microbiological research and laboratory techniques.
- Strong analytical skills and attention to detail.
- Proficiency in using laboratory equipment and software for data analysis.
- Excellent written and verbal communication skills.
Is becoming a Microbiologist a good career path?
Microbiology offers exciting career paths with a focus on understanding microorganisms. A microbiologist examines bacteria, viruses, and fungi to impact medicine, food safety, and environmental science. These professionals work in labs, research facilities, and various industries. They often collaborate with other scientists and contribute to significant advancements. The role demands strong analytical skills and attention to detail.
Working as a microbiologist comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. It’s important to consider both before pursuing this path. The pros include the chance to make a real difference in public health, opportunities for continuous learning, and potential for high-impact research. On the other hand, the cons include long hours in a lab, the need for precise and repetitive work, and the pressure to produce reliable results. Balancing these factors helps individuals decide if this career aligns with their skills and interests.
Here are some pros and cons to consider:
- Pros:
- Contributes to public health
- Opportunities for ongoing education
- Potential for impactful research
- Cons:
- Long hours in a lab
- Repetitive and detailed work
- High pressure to ensure accurate results
What is the job outlook for a Microbiologist?
Microbiologists study microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. This profession offers a stable and growing job outlook, making it a promising career path for job seekers. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that there are about 10,600 job openings for microbiologists each year. This number is expected to increase by 4.7% from 2022 to 2032. Such consistent growth reflects the ongoing demand for experts in this field.
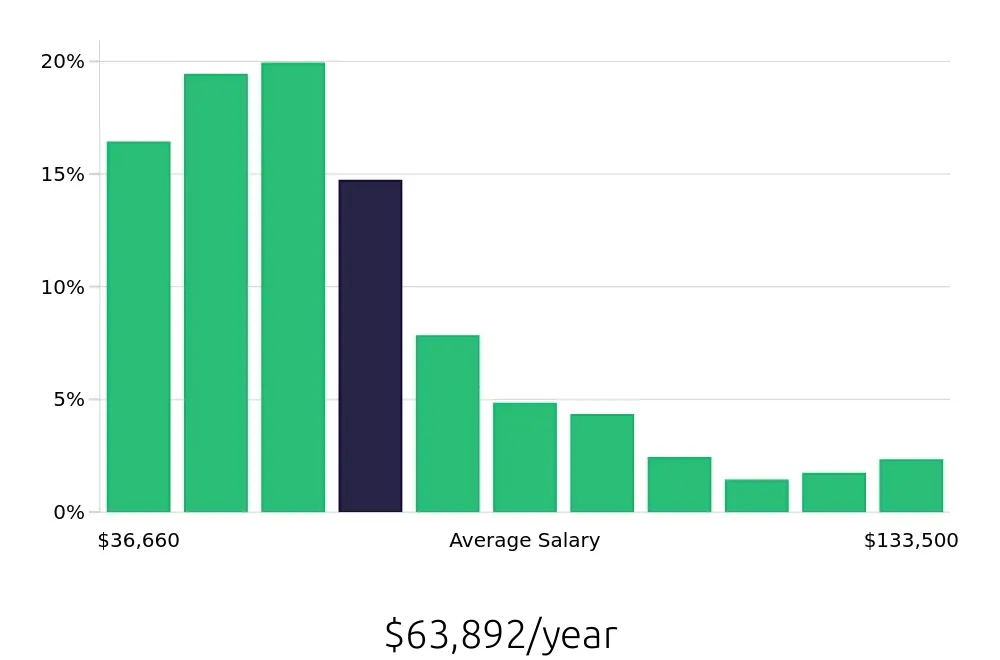
Microbiologists can find employment in various sectors, including healthcare, environmental science, and food safety. These roles are crucial for research and development, diagnostics, and ensuring public health safety. With an average annual salary of $100,440, microbiologists also enjoy a competitive compensation package. The hourly rate averages $48.29, making this a financially rewarding career choice. The diverse job opportunities and stable income make microbiology an attractive field for those looking to secure their future in science.
For those entering the job market, the microbiology sector offers a blend of stability and growth. The combination of steady employment opportunities and a respectable salary makes this career path a wise choice. With ongoing advancements in medical and environmental science, the demand for skilled microbiologists continues to rise. This trend ensures that professionals in this field will have ample chances to advance and make significant contributions to their industries.
Currently 83 Microbiologist job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Microbiologist