What does a Quality Engineer do?
A Quality Engineer plays a crucial role in ensuring that products meet specific standards and customer expectations. This professional works closely with manufacturing, design, and quality assurance teams to identify potential issues before products reach consumers. They analyze production processes and implement quality control measures to minimize defects. Quality Engineers conduct tests, inspections, and audits, ensuring that all parts meet safety and quality regulations.
Responsibilities of a Quality Engineer include creating and maintaining quality documentation, investigating and resolving quality issues, and recommending improvements in production methods. They also collaborate with cross-functional teams to solve quality-related problems and enhance overall product quality. By identifying trends and issues early in the production cycle, Quality Engineers help companies maintain high standards and reduce waste. Their work is essential for building and maintaining a company's reputation for quality and reliability.
How to become a Quality Engineer?
Becoming a Quality Engineer involves several key steps that can help ensure a successful career in the field. This profession requires a mix of technical knowledge, attention to detail, and the ability to work in a team. Here are five steps to take when pursuing a career as a Quality Engineer.
First, earn a relevant degree. Most employers look for candidates with at least a bachelor's degree in engineering, quality management, or a related field. This education provides the foundation needed to understand quality standards and processes. Second, gain hands-on experience through internships or entry-level positions. Working in a real-world setting helps develop practical skills and an understanding of industry standards.
- Earn a Relevant Degree - A degree in engineering, quality management, or a related field provides the necessary foundation.
- Gain Hands-On Experience - Internships or entry-level positions offer practical skills and industry knowledge.
- Obtain Certifications - Certifications such as ASQ's Certified Quality Engineer (CQE) enhance credibility and job prospects.
- Develop Key Skills - Skills such as problem-solving, attention to detail, and analytical thinking are crucial.
- Network and Apply - Connect with industry professionals and apply for relevant job openings to find the right position.
Third, obtain certifications to boost credibility and job prospects. Certifications such as the Certified Quality Engineer (CQE) from the American Society for Quality (ASQ) can set a candidate apart. Fourth, develop key skills that are essential for the role. These include problem-solving, attention to detail, and analytical thinking. Finally, network and apply for relevant job openings. Connecting with industry professionals and applying for positions will increase the chances of landing a job.
How long does it take to become a Quality Engineer?
The journey to becoming a Quality Engineer often starts with a solid educational foundation. Most employers look for candidates with at least a bachelor's degree in engineering, quality assurance, or a related field. This academic path typically takes about four years. Some may choose to further their education with a master’s degree, adding another two years to the timeline. Gaining hands-on experience through internships or entry-level positions can help speed up the process.
Experience plays a crucial role in the career progression of a Quality Engineer. Many professionals enter the workforce with a degree and work in entry-level roles to build their skills. On average, it takes about three to five years of relevant experience to move into a mid-level position. Further advancements to senior roles or specialized positions can take additional three to five years, depending on the industry and specific job requirements. Gaining certifications, such as the ASQ Certified Quality Engineer (CQE), can also enhance career opportunities and speed up promotions.
Quality Engineer Job Description Sample
We are seeking a highly skilled Quality Engineer to join our team. The ideal candidate will be responsible for ensuring that our products meet the highest quality standards and comply with all regulatory requirements. This role will involve working closely with cross-functional teams to identify, analyze, and resolve quality issues.
Responsibilities:
- Develop, implement, and maintain quality systems and procedures.
- Conduct quality audits and inspections of products and processes.
- Analyze quality data to identify trends and areas for improvement.
- Collaborate with cross-functional teams to resolve quality issues.
- Ensure compliance with all applicable regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in Engineering, Quality Management, or a related field.
- Minimum of 3 years of experience in a quality engineering role.
- Strong knowledge of quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100).
- Experience with statistical process control and quality improvement methodologies.
- Excellent analytical and problem-solving skills.
Is becoming a Quality Engineer a good career path?
A Quality Engineer plays a critical role in ensuring that products meet certain standards. This professional checks products at each stage of production to catch any errors. They work closely with the production team to solve any quality issues. This job requires attention to detail and problem-solving skills.
Quality Engineers often find work in manufacturing, automotive, and pharmaceutical industries. Companies need their expertise to maintain high standards. This career path can lead to roles with more responsibility, like Quality Manager. It offers a chance to improve processes and help companies grow. However, it can also come with some challenges, like dealing with tight deadlines or working long hours during product launches.
When considering this career, it helps to know the pros and cons. Let's look at some benefits first:
- Job stability: There is always demand for quality in manufacturing and other industries.
- Competitive salary: Quality Engineers often earn a good salary with benefits.
- Skills development: This job helps develop skills in problem-solving and attention to detail.
- Opportunities for advancement: Experience can lead to higher roles like Quality Manager.
Now, let's consider some challenges:
- Stressful deadlines: Meeting production schedules can be challenging.
- Long hours: Extra work may be needed during critical product launches.
- Frequent travel: Some roles require traveling to different locations to inspect products.
- Detail-oriented work: This job demands a lot of focus and precision.
What is the job outlook for a Quality Engineer?
Finding a stable and rewarding career is important for many job seekers. Quality Engineers play a vital role in ensuring product quality and efficiency. They examine manufacturing processes, identify areas for improvement, and develop testing protocols. The job outlook for Quality Engineers is positive, with an average of 24,100 positions available each year, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). This number reflects a projected growth of 11.2% from 2022 to 2032, which is higher than the average for all occupations.
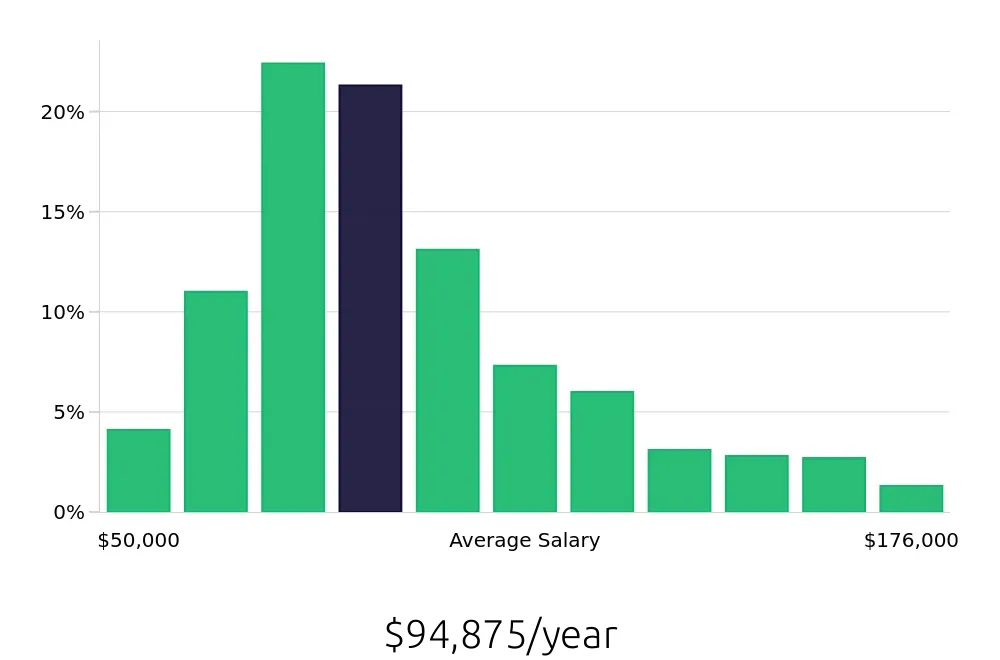
Quality Engineers can expect a strong compensation package to match their important work. The BLS reports an average national annual salary of $103,510 for Quality Engineers. This average salary reflects a stable and competitive pay scale for those in the field. In addition, the average national hourly compensation stands at $49.76. This hourly rate provides a clear picture of the financial rewards that can come with a career in quality engineering. Both salary and hourly rate offer excellent benefits for professionals in this sector.
With the growing emphasis on quality in manufacturing and production, the demand for Quality Engineers continues to rise. Companies across various industries rely on these professionals to ensure their products meet high standards. This steady demand for skilled Quality Engineers makes it an attractive career path for job seekers. The combination of strong job outlook, competitive salaries, and professional growth opportunities makes quality engineering an appealing choice for many.
Currently 1,108 Quality Engineer job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Quality Engineer