Position
Overview
A Repair Specialist plays a crucial role in maintaining and fixing equipment and machinery. This professional ensures that all systems run smoothly. They identify issues and perform necessary repairs. These specialists work in various settings, including factories, warehouses, and service centers.
The duties of a Repair Specialist involve diagnosing problems, repairing faulty parts, and testing equipment to ensure it functions correctly. They use tools and equipment to dismantle, inspect, and reassemble parts. Specialists also document repairs and maintenance activities. Their work helps prevent costly downtimes and keeps operations running efficiently. Regular communication with other team members is essential to coordinate repair efforts.
Becoming a repair specialist can lead to a rewarding career. It involves fixing and maintaining equipment and machinery. This role requires a mix of skills, including technical know-how and problem-solving abilities. Here is a simple guide to help someone start this career.
The path to becoming a repair specialist starts with gaining the right education. Most people need a high school diploma or GED. Some roles may require a post-secondary education, such as a certificate or associate’s degree in a related field. Technical schools and community colleges often offer these programs. These courses teach the basics of repair work and provide hands-on experience.
Interested in becoming a Repair Specialist? The journey involves a mix of education, training, and experience. Typically, one must first complete a high school diploma or GED. Many find it beneficial to enroll in a vocational or technical school program.
These programs often last from one to two years. During this time, students learn about machinery, electronics, and repair techniques. After completing formal education, hands-on experience is crucial. Many Repair Specialists start with an apprenticeship, working under a seasoned professional. This period can range from one to four years. Job seekers should expect to build a portfolio of skills and experiences to demonstrate their competency.
The Repair Specialist is responsible for diagnosing, repairing, and maintaining a variety of equipment and machinery within an industrial setting. This role requires technical expertise, problem-solving skills, and the ability to work independently or as part of a team to ensure minimal downtime and optimal performance of equipment.
Responsibilities:
Qualifications
A career as a Repair Specialist involves fixing and maintaining a variety of mechanical and electronic equipment. This role can span across different industries, from automotive to home appliances. Specialists use their technical skills to diagnose problems, make repairs, and ensure equipment runs smoothly. They often work in shops, on-site at businesses, or even in homes. This career path can lead to job satisfaction as one helps others by solving technical issues and extending the life of equipment.
Working as a Repair Specialist comes with its own set of advantages and challenges. Here are some pros and cons to consider.
Job seekers looking to enter the repair specialist field will find promising opportunities. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports an average of 21,100 job positions open each year. This figure highlights a consistent demand for skilled repair specialists across various industries. This outlook ensures a stable job market for those entering this profession.
The job outlook for repair specialists is positive, with a projected percent change in openings from 2022 to 2032 of 5.5%, according to the BLS. This growth suggests that more employers will need skilled repair specialists to maintain and repair equipment. This trend makes the repair specialist career path a good choice for job seekers seeking stability and growth. Opportunities are expected to increase, providing a secure future for those in this field.
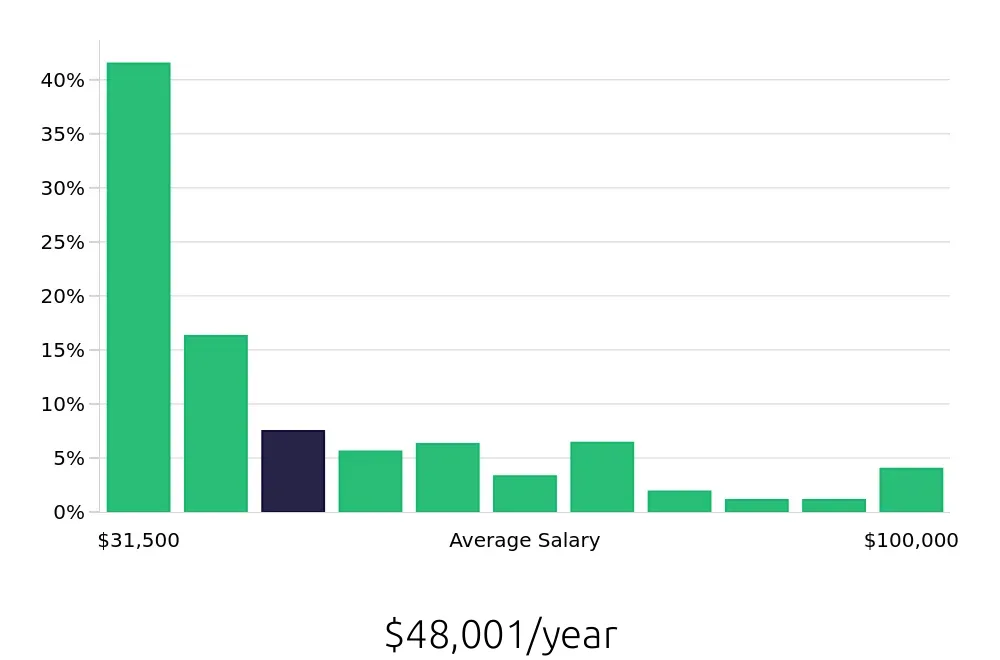
Repair specialists can also look forward to competitive compensation. The BLS reports an average annual salary of $62,520. On an hourly basis, this translates to $30.06. These figures indicate that repair specialists earn a good living. The combination of job stability and attractive compensation makes this career appealing to those looking for both job security and financial rewards.