Position
Overview
A Respiratory Therapist provides care to patients who have trouble breathing. They work with doctors to help people who have conditions like asthma, bronchitis, or pneumonia. They often work in hospitals, clinics, or nursing homes. They use machines to help patients breathe easier.
Respiratory Therapists set up and monitor equipment like oxygen tanks and ventilators. They clean and maintain machines to ensure they work well. They check patients' vital signs and keep records of their progress. They also educate patients on how to manage their conditions. This role requires strong communication skills and attention to detail. Respiratory Therapists must be able to work well under pressure and provide compassionate care.
Becoming a Respiratory Therapist is a rewarding career choice for those interested in healthcare. This path requires dedication and a few specific steps. Following the right steps can make the journey smoother and more successful.
The process includes completing the necessary education, gaining practical experience, and obtaining the required certifications. Below are the key steps to start this career.
Getting into the job market as a Respiratory Therapist offers a rewarding career path. Most people start by completing an accredited education program. This training usually takes about two years. Students learn about the respiratory system, how to use medical equipment, and how to care for patients. After finishing the program, they must pass a national exam.
After completing their education, many respiratory therapists gain practical experience. They often do this through internships or entry-level jobs. This experience helps them to apply what they learned in real-world settings. Some may also choose to get additional certifications. These can cover areas like neonatal care or critical care. While the exact timeline can vary, the average career path takes about four to six years from start to finish.
A Respiratory Therapist provides critical care to patients with breathing or cardiopulmonary disorders. They evaluate patients, develop treatment plans, and administer respiratory therapies to improve patients' lung function and overall health.
Responsibilities:
Qualifications
A career as a Respiratory Therapist offers the chance to help others in a meaningful way. This profession requires specialized training in the care of patients with breathing issues. Respiratory Therapists work in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities. They assist doctors by providing treatments and monitoring patients’ progress.
When considering this path, it is important to look at both the pros and cons. Working as a Respiratory Therapist has many benefits, such as helping patients improve their health and being part of a dedicated healthcare team. Additionally, this career often provides job stability and good pay. However, it also comes with challenges, like dealing with critically ill patients and working long hours. The job can be emotionally taxing, requiring strong empathy and communication skills.
Below are some important factors to consider:
Job seekers interested in becoming a Respiratory Therapist can look forward to a promising career path. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports an average of 51,700 job positions available per year. This number reflects a growing demand for respiratory care professionals. With a projected growth rate of 14.2% from 2022 to 2032, this field offers stability and opportunity. Job growth is driven by an aging population and increased awareness of respiratory health issues.
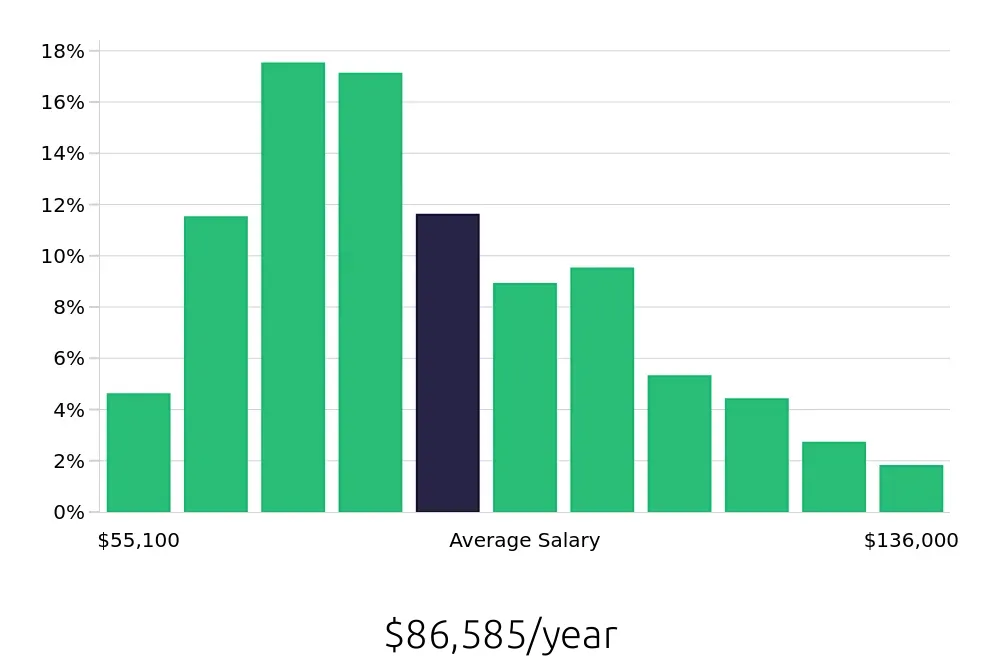
Respiratory Therapists enjoy competitive compensation. The BLS states that the average national annual salary is $92,670. Hourly rates are equally attractive, averaging $44.55 per hour. These figures indicate a rewarding career in terms of financial compensation. Higher salaries often come with better benefits, making this a lucrative choice for job seekers.
The demand for Respiratory Therapists remains strong. Hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities all need skilled professionals. The BLS data shows steady job openings each year. This trend offers job security and growth potential. Job seekers can look forward to many opportunities in this field.