What does a Revenue Agent do?
A Revenue Agent plays a crucial role in ensuring tax compliance by examining tax returns. They assess if individuals and businesses correctly report their income and pay the right amount of tax. This involves analyzing financial records, interviewing taxpayers, and applying tax laws accurately. Revenue Agents work for the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), a government agency responsible for tax collection.
To excel in this role, a Revenue Agent must have strong analytical skills. They need to review complex financial information and identify any discrepancies. Communication skills are also key, as they must explain tax laws and findings clearly to taxpayers. Integrity and attention to detail are essential qualities for someone in this position. They must ensure that all tax laws are followed and that everyone pays their fair share.
How to become a Revenue Agent?
Becoming a Revenue Agent involves several steps that test both knowledge and skills. This career path is ideal for someone who enjoys problem-solving and working in a dynamic environment. To start, one needs to understand the qualifications and steps required to achieve this role.
The journey to becoming a Revenue Agent begins with meeting the basic requirements. First, an individual must hold at least a bachelor's degree from an accredited university. This degree can be in any field, but some relevant subjects include accounting, finance, economics, or law. Second, a strong foundation in math and analytical skills is essential. Third, gaining experience in a related field, such as auditing or financial analysis, helps prepare for the responsibilities of the job. Fourth, developing a keen sense of ethics and integrity is crucial, as this role involves ensuring compliance with tax laws. Finally, understanding the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) policies and procedures is key. This can be achieved through additional training or certifications.
Once the basic requirements are met, the next steps involve applying and training. Start by visiting the official IRS website to find current job openings for Revenue Agent positions. Prepare a strong resume and cover letter that highlight relevant experience and qualifications. Apply through the USAJOBS platform, the official federal employment site. After submitting an application, be prepared for a series of interviews and assessments. These may include a written test, a panel interview, and a background check. Successful candidates then undergo training at the IRS Academy. This training covers federal tax laws, investigative techniques, and other necessary skills for the job.
- Hold a bachelor's degree from an accredited university.
- Develop strong math and analytical skills.
- Gain experience in a related field.
- Understand IRS policies and procedures.
- Apply through the USAJOBS platform and complete training at the IRS Academy.
How long does it take to become a Revenue Agent?
To start a career as a Revenue Agent, dedication and a solid educational foundation are key. Typically, it takes around three to four years of college to earn a bachelor’s degree. This degree can be in any field, but subjects like accounting, finance, and business administration are often preferred. Gaining experience in these areas will make the transition into a Revenue Agent role smoother.
After earning a degree, the next step involves working in a related field. Many Revenue Agents gain experience by working as auditors, accountants, or in tax preparation. This experience helps in understanding the nuances of tax laws and regulations. Once enough experience is accumulated, applying for the Revenue Agent position with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) becomes the next step. The hiring process includes a rigorous selection and training period, which typically lasts several months. This training is crucial, as it prepares new agents for the challenges of the job, ensuring they are well-equipped to handle their responsibilities effectively.
Revenue Agent Job Description Sample
A Revenue Agent is a tax professional responsible for ensuring compliance with tax laws by examining individual, business, and corporate tax returns for accuracy and completeness. They identify discrepancies, collect data, and take corrective action to recover any unpaid taxes.
Responsibilities:
- Conduct examinations of tax returns to identify discrepancies and non-compliance.
- Interview taxpayers and gather necessary documentation to support tax returns.
- Analyze financial data and income statements to determine the accuracy of tax filings.
- Prepare detailed reports and documentation of findings, maintaining thorough records.
- Collaborate with legal and other government agencies when necessary to resolve complex tax issues.
Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in Accounting, Finance, or a related field.
- Prior experience in tax examination, accounting, or auditing is highly desirable.
- Strong understanding of tax laws and regulations.
- Excellent analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Effective communication and interpersonal skills to interact with taxpayers.
Is becoming a Revenue Agent a good career path?
A Revenue Agent plays a key role in the financial oversight of a nation. This career involves auditing and reviewing tax returns to ensure compliance with tax laws. It demands a blend of analytical skills, attention to detail, and a strong understanding of financial regulations.
This role offers various opportunities for professional growth. Revenue Agents can advance to higher positions within the tax agency, or transition to related fields such as auditing or financial consulting. The career path provides a stable environment with the chance to make significant contributions to public service.
Considering the career of a Revenue Agent has its own set of advantages and challenges. Here are some pros and cons to think about:
- Pros:
- Job security: Federal employment offers stability and benefits.
- Competitive salary: Revenue Agents receive a good pay package.
- Professional growth: Opportunities for advancement are available.
- Public service: Contributing to the enforcement of tax laws can be rewarding.
- Cons:
- Stressful environment: The job can be demanding and high-pressure.
- Travel required: Agents may need to travel for audits and training.
- Long hours: The workload can be intensive, especially during tax season.
- Detail-oriented: The job requires a high level of accuracy and attention to detail.
What is the job outlook for a Revenue Agent?
Becoming a Revenue Agent offers a promising job outlook. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports an average of 16,500 job positions available each year. This consistent demand ensures opportunities for those entering the field. Furthermore, the BLS projects a modest 1.2% change in job openings from 2022 to 2032. This stability makes it a reliable career choice for many job seekers.
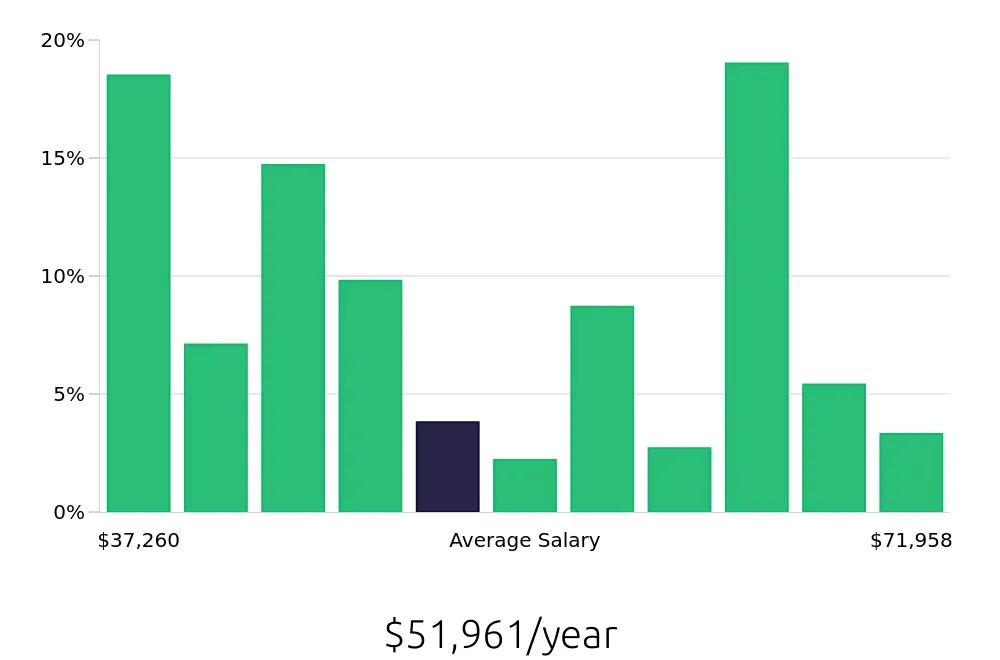
Revenue Agents benefit from competitive compensation. According to the BLS, the average national annual salary for this role is $60,900. This figure reflects the importance and skill level required for the job. Additionally, the average hourly wage stands at $29.28, providing a steady income for those in this position. These financial rewards make the role attractive to many professionals.
Job seekers will find a clear path with structured growth in this profession. The steady number of annual job openings and the projected stability in job openings over the next decade suggest a reliable career choice. Combined with competitive pay, the role of a Revenue Agent provides both job security and financial stability. This makes it an excellent opportunity for job seekers looking for a rewarding career.
Currently 39 Revenue Agent job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Revenue Agent