What does a Safety Engineer do?
A Safety Engineer plays a key role in ensuring a safe working environment. This professional assesses workplace hazards and implements safety measures to prevent accidents. They inspect buildings, equipment, and processes to identify risks. They also develop safety protocols and train employees on safety practices. Their goal is to minimize injury and illness in the workplace.
Safety Engineers analyze data to understand patterns and causes of accidents. They design safety equipment and systems to improve workplace safety. They also work closely with other departments to ensure safety standards are met. They stay updated on industry regulations and best practices. This role requires a strong understanding of safety laws and a commitment to protecting workers.
How to become a Safety Engineer?
Becoming a Safety Engineer involves gaining specific skills and education. This career path can lead to roles that ensure safety in the workplace. It requires dedication and the right steps. Follow the steps below to start this rewarding career.
First, start with a strong education foundation. Most Safety Engineers hold a bachelor’s degree in engineering or a related field. Programs often focus on industrial, mechanical, or chemical engineering. Some universities offer specialized safety engineering degrees. Completing this education provides the technical knowledge needed for the job.
- Earn a relevant degree. Obtain a bachelor’s degree in engineering or a related field.
- Gain practical experience. Work in internships or entry-level positions in safety or engineering roles.
- Consider certification. Obtain certifications such as Certified Safety Professional (CSP) or Occupational Health and Safety Technologist (OHST).
- Advance your education. Pursue a master’s degree or additional certifications to enhance skills and job prospects.
- Network and apply. Join professional organizations and attend job fairs to connect with potential employers.
Next, gain practical experience. Internships or entry-level jobs provide hands-on learning. Working in safety-related roles helps build essential skills. Experience is key to understanding workplace safety challenges and solutions. Consider certifications to boost credentials. Certifications like Certified Safety Professional (CSP) or Occupational Health and Safety Technologist (OHST) show dedication and competence.
How long does it take to become a Safety Engineer?
Safety engineers work to make workplaces safer. They look at how to prevent accidents. This job needs a strong knowledge of safety rules and standards. The time it takes to become one can vary. Most safety engineers have at least a bachelor’s degree in engineering or a related field. This education usually takes about four years.
After earning a degree, gaining practical experience is key. Many engineers work under a more experienced safety engineer. They might also gain experience in related fields. This training period can last from one to three years. Some engineers get certifications to boost their skills. Certifications can take several months to complete. Overall, it often takes between five to seven years to become a fully qualified safety engineer.
Safety Engineer Job Description Sample
We are seeking a dedicated Safety Engineer to join our team and ensure that all safety protocols are adhered to within our organization. The Safety Engineer will play a critical role in minimizing workplace hazards and implementing safety programs to create a safe work environment.
Responsibilities:
- Conduct regular safety inspections and audits of the workplace to identify potential hazards.
- Develop, implement, and manage safety policies and procedures.
- Investigate workplace accidents and incidents to determine causes and prevent future occurrences.
- Ensure compliance with local, state, and federal safety regulations and standards.
- Provide training and education to employees on safety protocols and procedures.
Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in Occupational Health and Safety, Engineering, or a related field.
- Certifications such as Certified Safety Professional (CSP), Occupational Hygienist (OH), or equivalent are preferred.
- Proven experience as a Safety Engineer or similar role.
- In-depth knowledge of occupational health and safety practices and regulations.
- Strong analytical and problem-solving skills.
Is becoming a Safety Engineer a good career path?
A career as a Safety Engineer focuses on making workplaces safer. This role involves identifying potential hazards, creating safety protocols, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations. Safety Engineers work in many industries, including manufacturing, construction, and healthcare. They aim to prevent accidents and protect workers from harm.
Choosing this career path has both advantages and challenges. For one, Safety Engineers make a positive impact by protecting people and reducing risks. They also enjoy job stability as safety is always a priority. However, this job can involve high stress, especially when dealing with dangerous situations. Safety Engineers must stay updated on laws and standards, which can require continuous learning.
Below are some pros and cons to consider:
- Pros:
- Helps prevent accidents and injuries.
- Job stability due to constant need for safety.
- Potential for good pay and benefits.
- Cons:
- Can be stressful when dealing with hazards.
- Requires staying updated on laws and regulations.
- May need to work long hours during inspections or emergencies.
What is the job outlook for a Safety Engineer?
Job seekers looking to enter the field of safety engineering will find a promising career path ahead. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the average number of job positions for safety engineers each year is around 24,100. This steady demand indicates a stable job market for professionals in this field. Additionally, the BLS predicts an 11.2% growth in job openings from 2022 to 2032, highlighting a positive trend for those considering a career as a safety engineer. This growth suggests increasing opportunities for those qualified in safety engineering.
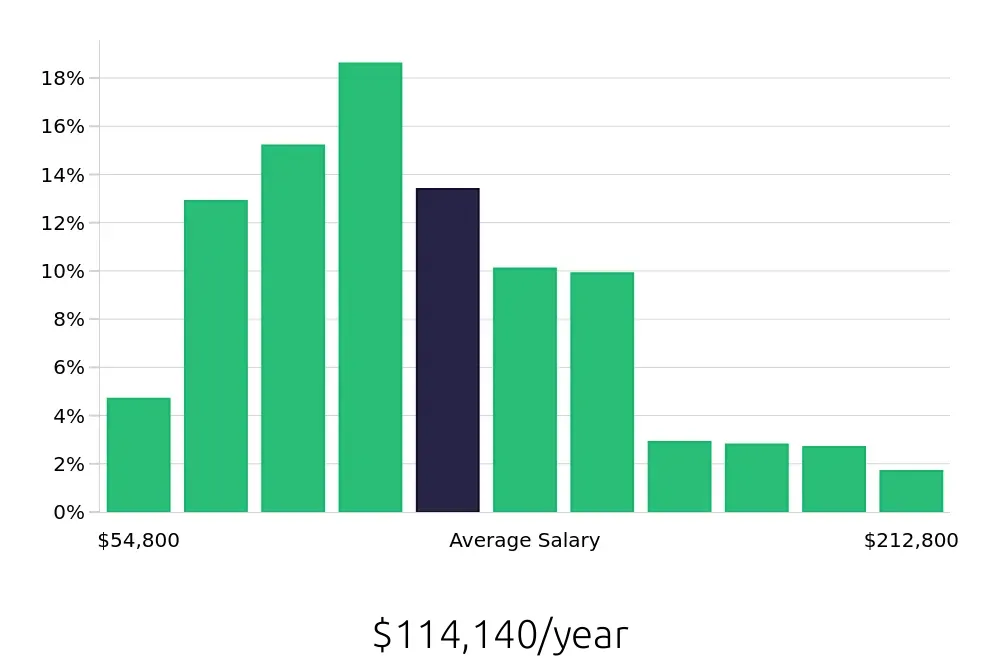
Safety engineers play a crucial role in ensuring workplace safety across various industries. Their work helps prevent accidents and reduce risks, making them valuable assets to any organization. With an average national annual compensation of $103,510, as reported by the BLS, safety engineers enjoy a competitive salary. This remuneration reflects the importance and demand for their expertise. Moreover, the average national hourly compensation is approximately $49.76, providing a clear picture of the financial benefits associated with this career choice.
For those entering the field, understanding the salary and job outlook can aid in career planning. The BLS data shows not only a good number of job positions available each year but also a positive growth trend. This combination makes safety engineering an attractive career option. Job seekers should consider these factors when evaluating potential career paths. The combination of stable job demand, salary potential, and growth opportunities makes safety engineering a compelling choice for professional development.
Currently 193 Safety Engineer job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Safety Engineer