What does a Site Reliability Engineer do?
A Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) plays a crucial role in ensuring that digital services run smoothly and efficiently. This professional works closely with development and operations teams to maintain the performance, availability, and scalability of applications. SREs are responsible for implementing practices like monitoring system health, developing automated tools to manage infrastructure, and responding swiftly to outages. They strive to balance reliability and productivity, ensuring that systems not only work but work well under all conditions.
SREs engage in various activities that help organizations stay ahead of potential issues. They design and execute tests to predict and mitigate failures. They also establish processes to automate repetitive tasks and improve the overall efficiency of system management. This role requires a strong background in software engineering and an understanding of both hardware and networking principles. SREs must be proactive in identifying bottlenecks and devising solutions that enhance system reliability. By doing so, they help ensure that services are resilient, scalable, and ready to meet the demands of users around the globe.
How to become a Site Reliability Engineer?
Becoming a Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) involves a blend of technical skills, hands-on experience, and a passion for problem-solving. This role is vital for ensuring that web services run smoothly and efficiently. An SRE must combine the best practices of software engineering with the principles of system administration. They work to prevent service outages and improve the reliability and performance of applications.
To embark on this career path, one needs to follow a structured process that builds both the necessary skills and experience. This journey can be broken down into five essential steps. Each step lays the foundation for the next, ensuring a thorough understanding and preparedness for the demands of the role.
- Acquire a solid educational background.
- Learn essential programming languages.
- Gain experience with system administration.
- Work on real-world projects.
- Get certified and continue learning.
Starting with a strong educational foundation, individuals should pursue a degree in computer science, software engineering, or a related field. This education provides a base understanding of the principles that SREs rely on daily.
Next, mastering key programming languages like Python, Java, or Go is crucial. These languages form the backbone of many modern applications and systems. Proficiency in these areas ensures that SREs can write efficient and effective code. Additionally, learning about system administration is essential. Understanding how to manage and maintain computer systems will help SREs to troubleshoot and optimize performance. Working on real-world projects, either through internships, personal projects, or contributions to open-source software, offers valuable practical experience. Finally, obtaining certifications in relevant technologies and continuously updating skills will keep SREs at the top of their game. This ongoing learning ensures that they stay current with industry trends and advancements.
How long does it take to become a Site Reliability Engineer?
The path to becoming a Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) often requires a blend of education and hands-on experience. Most candidates start with a bachelor’s degree in computer science or a related field. This typically takes about four years to complete. During this time, they should focus on courses that cover software development, networking, and systems administration.
After finishing a degree, gaining experience through internships or entry-level jobs is crucial. Many SREs spend about two to three years in these roles. They work closely with developers and operations teams, learning to maintain and improve systems. This period helps them build the skills needed for the SRE role. Some employers may prefer candidates with a master’s degree, which can take an additional one to two years. This advanced education often provides deeper knowledge and can make a candidate more competitive.
Site Reliability Engineer Job Description Sample
We are seeking a dedicated Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) to join our dynamic team. The ideal candidate will be responsible for ensuring the reliability, availability, and performance of our production systems, collaborating with development and operations teams to optimize infrastructure and automate processes.
Responsibilities:
- Design, develop, and maintain robust, scalable, and efficient systems to ensure high availability and performance.
- Implement monitoring, logging, and alerting systems to proactively identify and resolve issues.
- Develop and deploy automation tools to streamline operations, reduce manual intervention, and improve efficiency.
- Collaborate with development teams to implement best practices for CI/CD and infrastructure as code (IaC).
- Conduct post-mortem analyses on production incidents to identify root causes and develop preventive measures.
Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, Engineering, or a related field.
- Proven experience as a Site Reliability Engineer or similar role.
- Strong understanding of cloud platforms (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud, Azure) and container orchestration (e.g., Kubernetes).
- Proficiency in programming languages such as Python, Go, or similar.
- Experience with infrastructure as code tools (e.g., Terraform, CloudFormation).
Is becoming a Site Reliability Engineer a good career path?
A Site Reliability Engineer, or SRE, plays a key role in maintaining the stability and performance of systems. SREs blend software engineering skills with a focus on operations. They work to automate tasks and improve system reliability. This role often involves collaborating with both development and operations teams to ensure smooth operations and quick issue resolution.
The career path of an SRE offers many opportunities for growth and specialization. SREs can work in various environments, from small startups to large enterprises. This role often requires a solid understanding of both software engineering and system administration. SREs must be comfortable with scripting and automation, often using languages like Python or Go.
Here are some pros and cons to consider when thinking about a career as an SRE:
- Pros:
- Diverse skill set: SREs learn a lot about both development and operations.
- High demand: Many companies need SREs to keep their systems running smoothly.
- Problem-solving: SREs enjoy solving complex issues and improving system performance.
- Opportunities for growth: SREs can move into leadership roles or specialize in areas like cloud computing.
- Cons:
- Long hours: SREs often work irregular hours, including nights and weekends.
- High pressure: The role can be stressful, especially during system outages.
- Constant learning: Technology changes quickly, requiring continuous learning.
- Collaboration: SREs must work closely with different teams, which can be challenging.
What is the job outlook for a Site Reliability Engineer?
The demand for Site Reliability Engineers (SRE) is growing steadily. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports an average of 24,100 job positions each year. This role is crucial for maintaining the stability and reliability of IT systems. Companies rely on SREs to ensure their services run smoothly. This growing need highlights the importance of SREs in the tech industry.
Looking ahead, the job outlook for SREs is promising. BLS predicts an 11.2% increase in job openings from 2022 to 2032. This growth reflects the rising importance of cloud computing and digital transformation. Organizations need skilled SREs to manage their IT infrastructure effectively. This trend creates numerous opportunities for job seekers in this field.
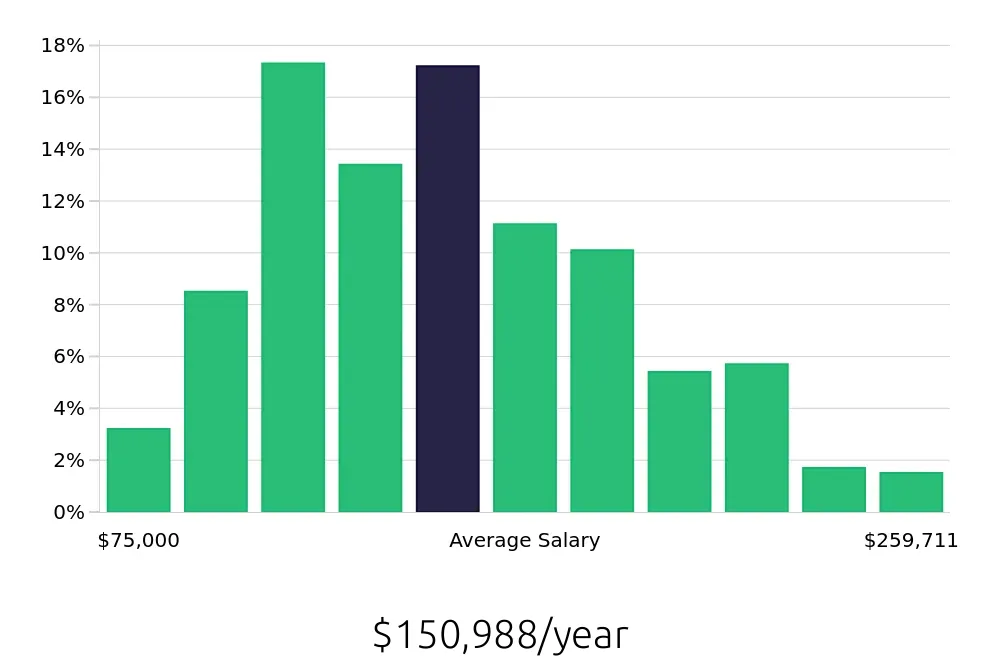
SREs also enjoy competitive compensation. According to the BLS, the average national annual salary for SREs is $103,510. The average hourly wage stands at $49.76. This strong financial incentive, combined with job stability, makes the SRE role attractive to professionals. For those seeking a rewarding and secure career, becoming an SRE offers excellent prospects.
Currently 120 Site Reliability Engineer job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Site Reliability Engineer