What does a Payroll Administrator do?
A Payroll Administrator manages the payroll process for an organization. This role involves processing employee pay, ensuring compliance with labor laws, and maintaining accurate payroll records. The Payroll Administrator works closely with both employees and management to ensure timely and accurate payment.
Key responsibilities include calculating employee wages, deductions, and benefits. This person coordinates with the HR department to ensure all payroll information is up-to-date. The Payroll Administrator also generates payroll reports and resolves any payroll-related issues. Attention to detail and strong organizational skills are essential in this role. Accuracy in processing payroll and meeting deadlines is crucial for maintaining employee satisfaction and compliance.
Typical duties of a Payroll Administrator involve:
- Calculating employee wages
- Handling payroll deductions
- Maintaining payroll records
- Ensuring compliance with laws
- Resolving payroll issues
How to become a Payroll Administrator?
Becoming a Payroll Administrator can open doors to many job opportunities. This role involves managing employee paychecks, taxes, and benefits. It requires accuracy and attention to detail. Here are key steps to start your career in payroll administration.
First, gain a high school diploma or equivalent. This is the minimum educational requirement. Next, enroll in a payroll administration course. Many community colleges and vocational schools offer such programs. They provide valuable knowledge about payroll systems and tax laws. This education sets a solid foundation for your career.
- Earn a High School Diploma or Equivalent: This is the starting point. Make sure your basic education is complete.
- Enroll in a Payroll Administration Course: Look for programs that offer hands-on training and real-world experience.
- Gain Experience: Look for entry-level positions in payroll departments. This helps you learn the job from the ground up.
- Obtain Certification: Consider getting a certification like the Certified Payroll Professional (CPP) or Certified Payroll Technician (CPT). This can boost your resume and career prospects.
- Stay Updated: Payroll laws and regulations change often. Keep up with the latest trends and updates in the field.
How long does it take to become a Payroll Administrator?
Interested in a career as a Payroll Administrator? This role is key in managing a company's employee pay and benefits. The path to this job can vary in length. Generally, it takes between one and four years to get started. This time can depend on a few key factors.
First, many employers prefer candidates with some college education. This often means completing an associate's degree in business or a related field. This path can take about two years. For those with a high school diploma, pursuing this degree can quickly open up job opportunities. Second, some payroll administrators gain experience through internships or entry-level office jobs. This can add another one to two years to the timeline. Working in these roles helps build skills in data entry, accounting, and attention to detail. Finally, some may choose to get certified. Certifications can enhance your resume and job prospects. They can take an additional six months to a year to complete.
In summary, the time it takes to become a Payroll Administrator can range from a year to four years. This will depend on your education, experience, and any additional certifications you choose to pursue. This career offers stability and good earning potential. With the right preparation, you can start your journey in payroll administration in a manageable timeframe.
Payroll Administrator Job Description Sample
We are seeking a meticulous and detail-oriented Payroll Administrator to join our finance team. The ideal candidate will be responsible for managing the payroll process, ensuring accuracy and compliance with legal requirements, and providing timely support to employees and management.
Responsibilities:
- Manage the end-to-end payroll process including data entry, calculations, and distribution of payroll.
- Ensure accurate and timely processing of payroll in accordance with company policies and legal requirements.
- Maintain employee payroll records and ensure confidentiality of employee information.
- Handle payroll-related inquiries and provide support to employees and management.
- Prepare and process payroll tax filings and ensure compliance with federal, state, and local regulations.
Qualifications
- Bachelor's degree in Accounting, Finance, or a related field.
- Minimum of 3 years of experience in payroll administration.
- Proven knowledge of payroll laws and regulations.
- Proficiency in payroll software and Microsoft Office Suite.
- Strong attention to detail and accuracy.
Is becoming a Payroll Administrator a good career path?
Working as a Payroll Administrator offers a stable career path filled with responsibilities that ensure employees receive their compensation correctly and on time. This role involves managing payroll processes, including calculating employee pay, withholding taxes, and distributing paychecks. Payroll Administrators often work closely with HR departments, ensuring compliance with labor laws and company policies.
Payroll Administrators often enjoy a mix of routine tasks and problem-solving challenges. They interact with employees, making this role suitable for those who enjoy a people-focused environment. However, it’s important to consider both the benefits and challenges of this career path.
Here are some pros and cons to think about:
- Pros:
- You can work in various industries, offering flexibility.
- Payroll tasks are routine, providing stability and predictability.
- Accurate payroll management is crucial for business operations.
- You gain valuable experience in finance and human resources.
- Cons:
- Payroll deadlines can be stressful, especially at the end of the month or quarter.
- You must keep up with changing labor laws and tax regulations.
- Working with sensitive employee information requires a high level of confidentiality.
- The job can be repetitive, which might not appeal to everyone.
What is the job outlook for a Payroll Administrator?
Becoming a Payroll Administrator offers a stable and rewarding career path, with ample opportunities available. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports an average of 137,700 job positions each year. This means there are plenty of chances for job seekers to enter the field. While the job openings are expected to decrease by 5.2% from 2022 to 2032, the role remains crucial in managing employee compensation.
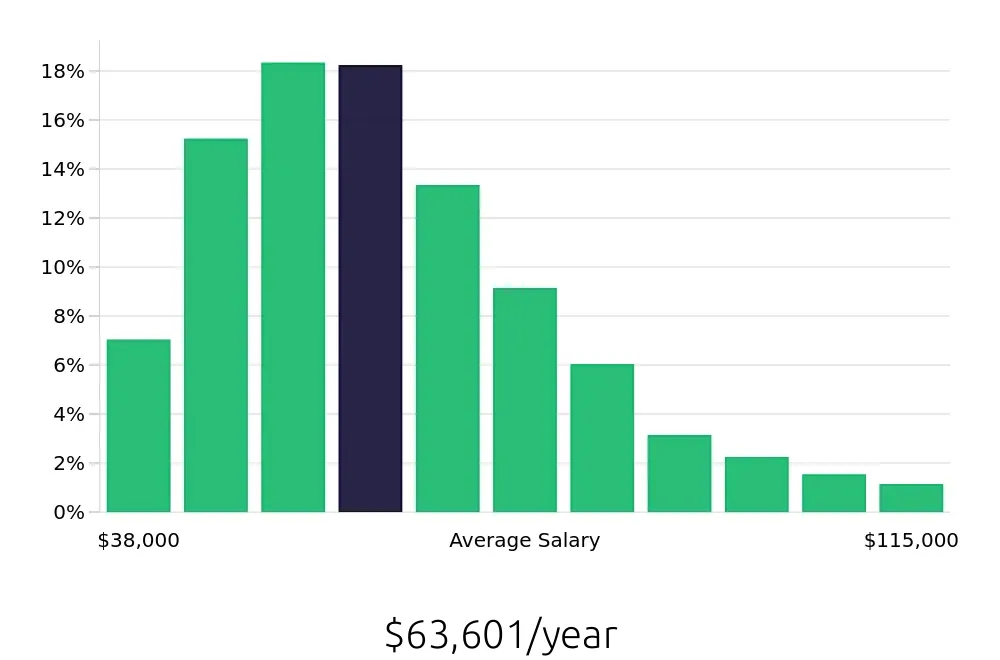
Payroll Administrators enjoy a solid average annual compensation of $68,620, according to the BLS. This figure reflects the national average and highlights the financial benefits of this career. On an hourly basis, professionals can expect to earn around $33.00. This competitive pay makes the role attractive to many, particularly those seeking stability and a steady income.
The path to becoming a Payroll Administrator involves gaining relevant skills and experience. Many employers prefer candidates with a high school diploma and some college coursework. Experience with payroll software and knowledge of labor laws are also important. With the right qualifications, job seekers can find good opportunities and grow in this field.
Currently 213 Payroll Administrator job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Payroll Administrator