What does a Quantitative Analyst do?
A Quantitative Analyst uses math and statistics to solve complex problems. They collect and analyze data to help businesses make smart decisions. This position often works in finance, investment, or risk management. The analyst builds models to predict trends and measure performance. They use their findings to guide investment strategies or manage financial risks.
Daily tasks for a Quantitative Analyst include gathering data from various sources. They then use statistical software to analyze this information. This job requires strong problem-solving skills and attention to detail. The analyst must also communicate their findings clearly. They work closely with other teams to ensure their models are accurate and useful. This role demands a solid understanding of financial markets and quantitative methods.
How to become a Quantitative Analyst?
Becoming a Quantitative Analyst (QA) involves gaining the right education, skills, and experience. This career path demands a solid understanding of mathematics, statistics, and computer programming. It also requires problem-solving abilities and a knack for analyzing data to help businesses make informed decisions.
The journey to becoming a Quantitative Analyst consists of several key steps. Follow these steps to establish a successful career in this field.
- Earn a Bachelor’s Degree: Start with a strong academic foundation. Study finance, economics, mathematics, or computer science. A degree in one of these areas provides the necessary background knowledge.
- Master Advanced Math and Statistics: Quantitative Analysts need to be proficient in advanced mathematics and statistics. Take courses in calculus, linear algebra, probability, and statistics. Understanding these concepts deeply is crucial.
- Learn Programming Skills: Develop skills in programming languages such as Python, R, or MATLAB. These tools are essential for analyzing data and creating models. Many employers look for candidates who can write clean, efficient code.
- Gain Experience: Look for internships or entry-level positions in finance, data analysis, or risk management. Experience in these areas helps build practical skills and makes the resume more attractive to future employers.
- Pursue Certifications: Consider obtaining certifications like the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) or the Financial Risk Manager (FRM). These credentials can enhance job prospects and demonstrate expertise.
How long does it take to become a Quantitative Analyst?
Pursuing a career as a Quantitative Analyst often requires a solid educational foundation and specialized skills. Most professionals in this field hold at least a bachelor’s degree in finance, economics, statistics, mathematics, or a related discipline. This initial education usually takes four years to complete. Employers often look for candidates with strong analytical and problem-solving abilities, as well as proficiency in programming languages like Python or R.
After completing their undergraduate studies, many Quantitative Analysts gain experience through internships or entry-level positions. This can add an additional one to two years to the timeline. Obtaining relevant certifications, such as the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) or the Financial Risk Manager (FRM), can further enhance job prospects. These certifications typically require passing exams and relevant work experience. Completing these steps often takes an additional one to two years. In total, it generally takes five to seven years from starting undergraduate studies to becoming a fully qualified Quantitative Analyst.
Quantitative Analyst Job Description Sample
We are seeking a skilled Quantitative Analyst to join our dynamic finance team. The ideal candidate will leverage advanced mathematical, statistical, and programming skills to develop and implement quantitative models that drive strategic decision-making. This role requires a strong analytical mindset, attention to detail, and the ability to work collaboratively in a fast-paced environment.
Responsibilities:
- Develop and implement quantitative models and algorithms to analyze financial data.
- Conduct thorough data analysis to support trading strategies and risk management.
- Collaborate with traders, risk managers, and other stakeholders to understand business requirements and translate them into quantitative solutions.
- Perform quantitative research to identify new opportunities and improve existing models.
- Validate and test models for accuracy and efficiency, ensuring they meet internal and regulatory standards.
Qualifications
- Bachelor’s degree in Mathematics, Statistics, Economics, Finance, Computer Science, or a related field. Master’s degree or Ph.D. is preferred.
- Proven experience as a Quantitative Analyst or similar role in a financial institution.
- Strong proficiency in programming languages such as Python, R, or C++, and experience with financial modeling software.
- In-depth understanding of statistical methods, mathematical modeling, and financial theory.
- Excellent problem-solving skills and the ability to think critically and analytically.
Is becoming a Quantitative Analyst a good career path?
A Quantitative Analyst uses math and computer skills to make smart financial decisions. They analyze data to help companies make better choices. This role combines skills in finance, math, and computer science. It offers exciting challenges and growth opportunities.
Working as a Quantitative Analyst has its perks and challenges. Here are some things to consider. On the positive side, the job pays well. Analysts often earn a good salary. They work with cutting-edge technology. This makes the work interesting and engaging. Analysts have the chance to make a real impact. Their work helps companies succeed. But the job is not without its challenges. The work can be very demanding. Analysts often have to handle large amounts of data. They must work under pressure to meet deadlines. The job requires strong math and computer skills. This can be tough for some people.
Here are some pros and cons of being a Quantitative Analyst:
- Pros:
- Good pay
- Opportunities for growth
- Interesting and challenging work
- Chance to make a real impact
- Cons:
- High demand for skills
- Heavy workload
- Need for strong math and computer skills
What is the job outlook for a Quantitative Analyst?
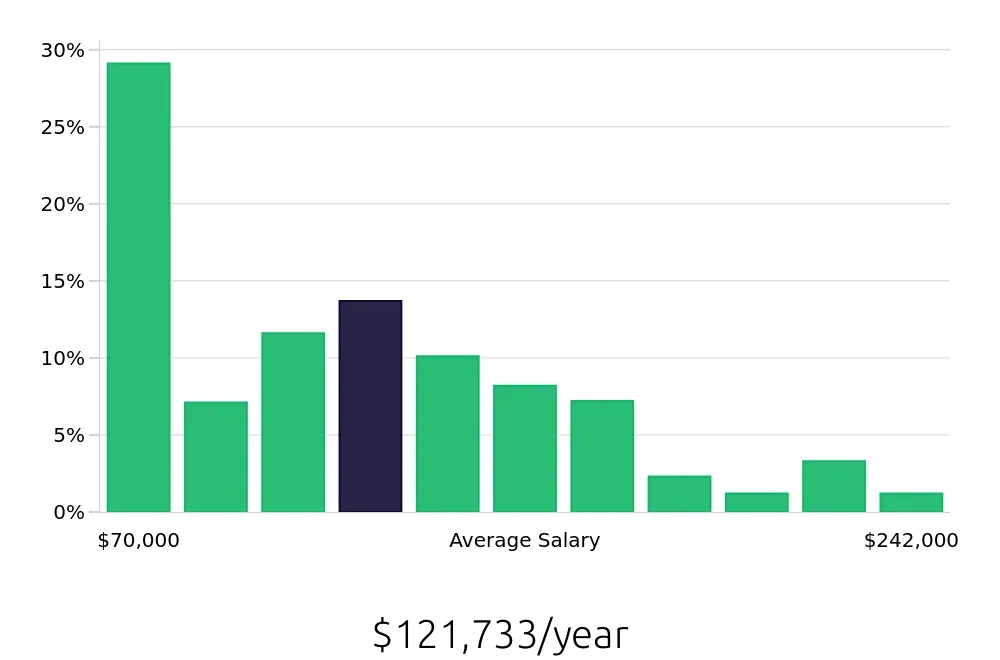
The job outlook for Quantitative Analysts is promising for anyone seeking a career in this field. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports an average of 9,900 job positions available per year. This consistent demand makes it a stable career choice. The projected percent change in job openings from 2022 to 2032 is a positive 6.1%. This growth suggests that more Quantitative Analyst roles will become available over the next decade. With the demand steadily rising, the field offers a solid future for job seekers.
Prospective Quantitative Analysts can also look forward to competitive compensation. According to the BLS, the average national annual salary stands at $89,650. This figure indicates that the role is well-compensated. Hourly compensation averages around $43.1. These numbers reflect the value employers place on skilled Quantitative Analysts. With both job growth and strong pay, this career path is highly attractive for those with the necessary skills.
A career as a Quantitative Analyst offers job seekers stability, growth, and strong earnings. The BLS data highlights a positive job outlook with an average of 9,900 positions annually and a 6.1% increase in job openings expected by 2032. The average national salary of $89,650 and hourly rate of $43.1 further underscore the appeal of this career. For anyone considering this path, the outlook is promising and rewarding.
Currently 119 Quantitative Analyst job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Quantitative Analyst