What does a Tax Analyst do?
A Tax Analyst plays a vital role in managing an organization's tax responsibilities. This professional examines and interprets tax regulations. They ensure the company complies with federal, state, and local tax laws. Tax Analysts prepare and review tax documents. They calculate tax liabilities and manage tax payments. This role requires a keen attention to detail and strong analytical skills.
In this position, the Tax Analyst conducts thorough tax research. They analyze financial data to identify tax savings opportunities. They often work closely with auditors and accountants. The Tax Analyst assists in tax audits and reviews. They prepare detailed tax reports and presentations for senior management. This role helps ensure the company remains compliant and financially efficient. It requires excellent organizational skills and the ability to work under pressure.
How to become a Tax Analyst?
Becoming a Tax Analyst can open doors to a rewarding career in finance. This profession involves analyzing financial data, preparing tax reports, and ensuring compliance with tax laws. The role requires strong analytical skills and attention to detail. Follow these steps to start your journey as a Tax Analyst.
First, gain a solid educational foundation. Most Tax Analysts hold at least a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or a related field. This education provides essential knowledge of financial principles and tax regulations. Completing coursework in statistics and computer science can also be beneficial. After obtaining a degree, consider obtaining relevant certifications, such as the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Enrolled Agent (EA) credentials. These certifications enhance credibility and job prospects.
- Earn a degree in accounting or finance.
- Obtain relevant certifications.
- Gain experience through internships or entry-level positions.
- Develop strong analytical and computer skills.
- Network and seek job opportunities.
Gaining practical experience is crucial. Internships and entry-level positions in accounting firms or corporate finance departments provide hands-on experience. Working under seasoned professionals helps to learn the nuances of tax analysis and builds a solid resume. During this time, focus on developing key skills, such as proficiency in financial software and strong analytical abilities. Networking with industry professionals through job fairs, seminars, and professional organizations can lead to job opportunities. Building a professional network enhances career prospects and provides insights into the industry.
How long does it take to become a Tax Analyst?
Becoming a Tax Analyst involves several steps. Most start with a bachelor’s degree in accounting, finance, or a related field. This usually takes about four years to complete.
After earning a degree, new analysts often need to gain experience. This can take one to two years. Some people do internships or entry-level jobs while they study. Others find part-time work to build their skills. Working under a seasoned tax professional can help a lot. It gives practical experience and a better understanding of tax laws.
Many tax analysts also choose to get certified. Options include the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or the Enrolled Agent (EA) designation. These certifications can take extra time to earn. They show a higher level of expertise and can lead to better job opportunities.
Tax Analyst Job Description Sample
The Tax Analyst will play a crucial role in assisting with the preparation and analysis of tax returns, ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations. This role involves working closely with accounting teams and tax professionals to identify tax savings opportunities and manage tax-related documentation.
Responsibilities:
- Prepare and review tax returns, ensuring accuracy and compliance with federal, state, and local tax laws.
- Analyze financial data to identify tax-related issues and recommend solutions.
- Coordinate with internal and external auditors during tax audits and examinations.
- Assist in the development and maintenance of tax policies and procedures.
- Provide support during the annual audit process, including the preparation of audit schedules and documentation.
Qualifications
- Bachelor's degree in Accounting, Finance, or a related field.
- Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Enrolled Agent (EA) designation preferred.
- Minimum of 2-4 years of experience in tax preparation and compliance.
- Strong knowledge of federal, state, and local tax laws and regulations.
- Proficiency in tax software and Microsoft Office Suite.
Is becoming a Tax Analyst a good career path?
A career as a Tax Analyst provides a stable path for those with a knack for numbers and a keen interest in financial regulations. Tax Analysts play a crucial role in ensuring that individuals and businesses comply with tax laws. They prepare tax returns, manage financial records, and provide advice on tax planning strategies. This role offers a mix of analytical tasks and direct interaction with clients, making it suitable for those who enjoy problem-solving and attention to detail.
Working as a Tax Analyst comes with its unique set of pros and cons. On the positive side, the role often offers a steady job with the potential for growth. Tax Analysts can advance to senior positions or specialize in areas like corporate or international tax. The job also provides a clear career progression, with opportunities for professional certifications like the Certified Public Accountant (CPA) or Enrolled Agent (EA). On the downside, the workload can be heavy, especially during tax season. Tax Analysts may also face the pressure of dealing with complex tax laws and regulations.
Here are some pros and cons to consider:
- Pros:
- Steady job with potential for growth
- Opportunities for professional certifications
- Clear career progression
- Cons:
- Heavy workload during tax season
- Dealing with complex tax laws and regulations
What is the job outlook for a Tax Analyst?
The job outlook for Tax Analysts is stable, making it an attractive career path. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), there are about 16,500 job positions available each year. This trend reflects a steady demand for professionals who can manage and analyze tax data. Job seekers can find a consistent number of opportunities, ensuring a reliable path for career growth.
The BLS also projects a 1.2% growth in job openings for Tax Analysts from 2022 to 2032. This growth rate indicates a positive job market with steady advancement possibilities. As businesses and individuals continue to navigate complex tax regulations, the need for skilled Tax Analysts will remain strong. This outlook is ideal for those seeking long-term employment stability and opportunities for advancement.
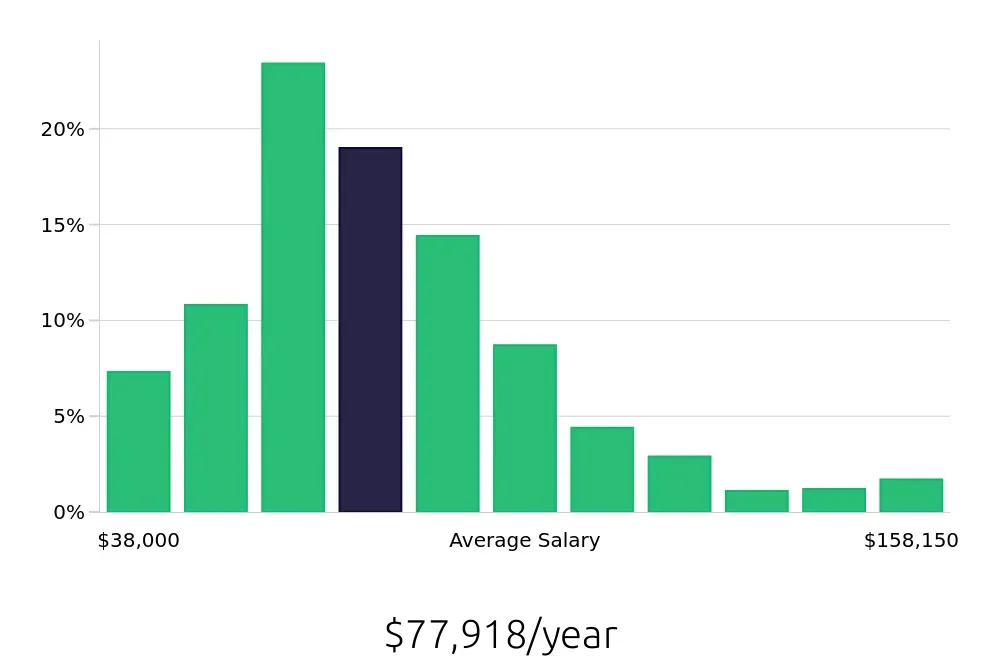
Tax Analysts earn a competitive salary, with an average annual compensation of $60,900, as reported by the BLS. The average hourly wage stands at $29.28, reflecting the value of their expertise. This compensation level offers a rewarding financial incentive for professionals in this field. Job seekers can expect a good return on their investment in education and training for a career as a Tax Analyst.
Currently 65 Tax Analyst job openings, nationwide.
Continue to Salaries for Tax Analyst